Relevance: GS II & III: IR and Sci & Tech
Introduction
India conducted Operation Sindoor, the biggest cross-border attack against terrorist infrastructure since Balakot, in retaliation to the Pahalgam terror attack. India asserted its right to react, prevent, and discourage similar cross-border assaults in the future.
About Pahalgam terrorist attack
About 40 visitors were the target of a vicious terrorist attack in the Baisaran meadows close to Pahalgam. According to witnesses, the attackers employed small arms and automatic firearms, apparently confirming the victims’ religious identity before carrying out a close-range execution. Since Article 370 was repealed in 2019, this is the first significant terror strike in Kashmir that targets civilians.
Lashkar-e-Taiba affiliate the Resistance Front (TRF) has taken credit for the event. As a move toward changing the region’s demographics, TRF said in its statement that it was against issuing 85,000 domicile certificates to non-locals. Security organizations have not yet confirmed the veracity of this assertion, though.
About Operation Sindoor
India initiated Operation Sindoor after the Pahalgam terror attack. The operation targeted terror camps in Pakistan and Pok. Indian forces struck nine terror-linked sites. Pakistan has placed its air force on high alert. Air travel in northern India faces major disruptions. US President Donald Trump has called for calm.
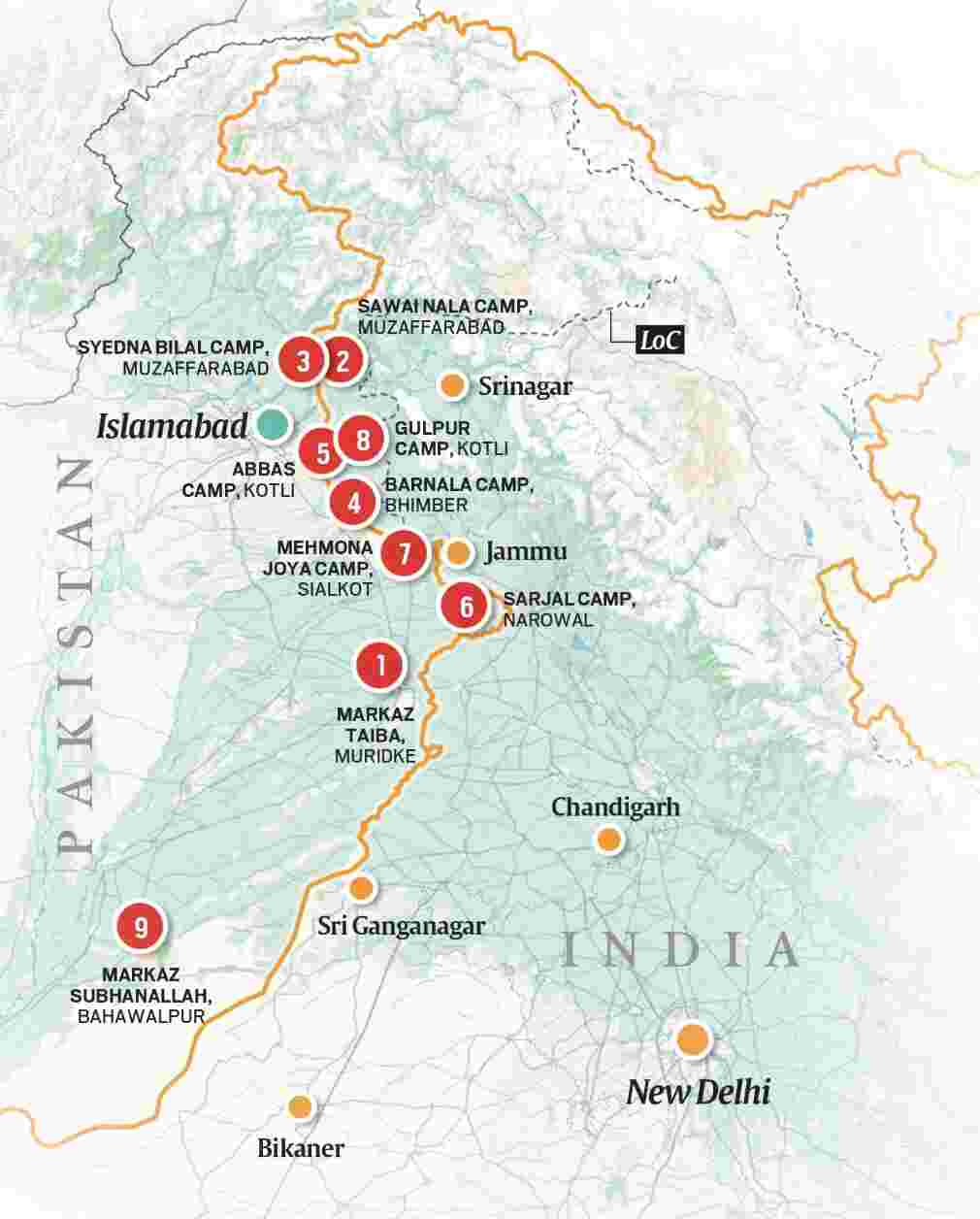
The 9 Terror Camps Targeted by India in Pakistan and PoK under Operation Sindoor
The targets were selected “based on credible intelligence inputs” in order to prevent any civilian casualties or damage to civilian infrastructure.
Camp Name & Location | Key Details |
Markaz Taiba, Muridke | Headquarters of Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT), led by Hafiz Saeed. 200-acre ideological nerve centre. Funded by Osama bin Laden. Trained 26/11 attackers. Located 18–25 km from IB. |
Sawai Nala camp, Muzaffarabad | Major LeT training site in PoK. Trained Pahalgam, Sonmarg, and Gulmarg attackers. Operational since 1990s. Temporarily shut post 9/11 and 26/11. |
Syedna Bilal camp, Muzaffarabad | Used by Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM) and LeT. Located on Neelum river. Recruits trained by Pakistani Special Forces (SSG). Jungle and explosives training centre. |
Barnala camp, Bhimber | Training camp near LoC for LeT and JeM. Specialized in jungle/mountain warfare and IEDs. Used as a launchpad for infiltrators. |
Abbas camp, Kotli | JeM fidayeen (suicide attacker) training centre. Provides CQB, breaching, hostage drills, and martyrdom indoctrination. Located near Kotli military base. |
Sarjal camp, Narowal | Regrouping camp near IB in Punjab. Located in a health centre. Linked to 2025 Kathua attack. Used for staging before advanced training in PoK. |
Mehmona Joya camp, Sialkot | Hizbul Mujahideen induction and launchpad site. Located 12–18 km from IB. Infiltration point via Punjab and Jammu regions. |
Gulpur camp, Kotli | LeT base for operations in Rajouri and Poonch. Trained attackers of 2023 and 2024. Functions in guerrilla warfare; reduced overt activity post-2016. |
Markaz Subhanallah, Bahawalpur | JeM headquarters. Masood Azhar’s base. 15-acre complex with elite facilities. Linked to Pathankot (2016) and Pulwama (2019) attacks. Near 31 Corps HQ. |
Execution of the Operation
The weapons deployed in Operation Sindoor early on Wednesday morning (May 7) have not been disclosed by India. According to the official release, the Indian Armed Forces attacked terrorist infrastructure in Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK) and deep within Pakistan with accurate strikes.
The Indian military has amassed an impressive collection of cutting-edge weaponry over the last few years, including drones, loitering munitions, and precision-guided long-range weapons. Among them:
Military equipment used
Weapon System | Key Features |
HAMMER | Air-to-ground precision-guided weapon for Rafale; range up to 70 km; made by Safran (France); autonomous, jamming-resistant, deployable at low altitudes. |
SCALP | Air-launched cruise missile with stealth; range ~450 km; built by MBDA; low-flying, night/all-weather capable; uses INS, GPS, and terrain referencing. |
METEOR | Beyond Visual Range Air-to-Air Missile (BVRAAM); effective in dense EW environments; ramjet-powered for long thrust and large ‘No Escape Zone’; made by MBDA. |
BRAHMOS | Supersonic cruise missile by DRDO & Russia’s NPO; Mach 3 speed; Fire and Forget; used by all three defence services; land/sea versions now have extended ranges. |
Technology and Strategy
India struck air defense installations in various Pakistani areas on Thursday morning after successfully preventing Pakistani strikes on multiple Indian targets overnight.
As the IAF activated its Integrated Counter UAS (Unmanned Aerial Systems) Grid and other air defense systems to stop Pakistan’s attacks on 15 military bases and multiple cities Thursday (May 8), India’s flagship surface-to-air missile systems—the S400 Triumf, Barak 8 MRSAM (Medium Range Surface to Air Missile), and the indigenous Akash—played a crucial role.
How Air Defence Systems work
Eliminating threats from the air, whether they be missiles, unmanned drones, or enemy fighter aircraft, is the main goal of an air defense system. A sophisticated network of radar, control centers, defensive fighter aircraft, and ground-based air defense missile, artillery, and electronic warfare weapons are used to accomplish this.
Operation Component | Description |
DETECTION | Initial step using radar or satellites to identify threats. Radars send electromagnetic waves that bounce off objects to determine location, speed, and type of threat. |
TRACKING | Ongoing observation of threats using radar, infrared sensors, and laser rangefinders. Enables the system to differentiate between multiple targets and maintain constant awareness. |
INTERCEPTION | Final action to neutralise threats based on tracking data. Method varies with threat type, range, and speed. Involves deployment of weapons like missiles or fighter aircraft. |
C3 (Command, Control, Communication) | Integrates detection, tracking, and interception. Facilitates real-time coordination, superior decision-making, and ensures system-wide efficiency. |
FIGHTER AIRCRAFT | Used as interceptors to neutralise enemy aircraft. Fast, agile jets scrambled to engage and destroy threats like bombers before they release payloads. |
Geopolitical Reactions
1. United States
According to US President Donald Trump, he hopes the fighting ends “very quickly.”
“It’s a shame,” he said while speaking to reporters in the White House, adding, “We heard about it just as we were walking in the doors of the Oval (Office). I guess people knew something was going to happen based on a little bit of the past.”
2. China
In reaction to a significant escalation between its nuclear-armed neighbors, China has voiced alarm over Indian strikes on Pakistan and urged both sides to exercise caution.
3. Russia
In the deadliest clash between the nuclear-armed neighbors in 20 years, India and Pakistan exchanged heavy artillery fire after New Delhi launched devastating missile strikes. Moscow has urged both countries to exercise “restraint” in the conflict.
4. United Kingdom
Trade Secretary Jonathan Reynolds stated on Wednesday that the UK is prepared to assist both India and Pakistan in defusing the situation.
5. Israel
Following missile attacks on Pakistan, Israel has supported “India’s right to self-defense.” Israel “supports India’s right for self-defence,” said Israeli Ambassador to India Reuven Azar on X, adding that “Terrorists should know there’s no place to hide from their heinous crimes against the innocent.”
PYQ:
- “Increasing cross-border terrorist attacks in India and growing interference in the internal affairs of several member-states by Pakistan are not conducive for the future of SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation).” Explain with suitable.
UPSC General Studies Paper Preparation
Topic | |
About the Author: Nitin Kumar Singh |



