Bhoj Wetland
Why in News: The Union Government recently clarified that the Bhoj Wetland in Bhopal, an international Ramsar site, is not at risk of being delisted from the Ramsar Convention list of wetlands of international importance.
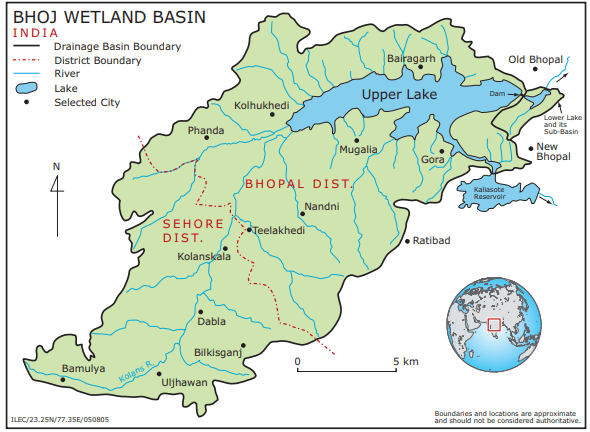
About Bhoj Wetland:
- Location: Situated in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, Bhoj Wetland comprises two connected man-made reservoirs: the Upper Lake, known as Bhojtal (Bada Talaab), and the Lower Lake, referred to as Chhota Talaab.
- Surroundings: The Upper Lake is bordered by Van Vihar National Park to the south, residential areas to the east and north, and agricultural fields to the west. It serves as a crucial source of drinking water for Bhopal.
- Biodiversity: The lakes are rich in biodiversity, particularly in macrophytes, phytoplankton, and zooplankton. They are home to over 15 species of fish and several vulnerable species, including turtles, amphibians, and aquatic invertebrates.
- Ramsar Site Designation: Bhoj Wetland was designated as a Ramsar site in 2002, recognizing its international importance as a wetland.
What is the Ramsar Convention?
- The Ramsar Convention is an international treaty signed on 2nd February 1971, aimed at conserving the ecological character of wetlands of global significance.
- Named after Ramsar, the Iranian city where the treaty was signed, wetlands selected for conservation under this treaty receive the designation of “Ramsar site.”
National Coastal Mission Scheme
Why in News: Recently, the Minister of State for Environment, Forest, and Climate Change provided information to the Lok Sabha regarding the National Coastal Scheme.

About National Coastal Mission Scheme:
- Launch Year: The scheme was launched in 2014.
- Purpose: It is envisioned under the National Action Plan on Climate Change to address the impact of climate change on coastal and marine ecosystems, infrastructure, and communities in coastal regions through adaptation and mitigation strategies.
Components:
- Conservation Initiatives: Management Action Plan for the conservation of mangroves and coral reefs.
- Research & Development: Focused on the marine and coastal ecosystems.
- Sustainable Beach Development: Under the Beach Environment & Aesthetic Management Service.
- Capacity Building: Outreach programs for coastal states/UTs on conservation, including beach cleaning drives.
- Implementation: The scheme is implemented by the State Governments of Coastal States and Union Territory (UT) Administrations.
Key Facts About National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC):
- Launch Date: The NAPCC was formally launched on June 30th, 2008.
- Objective: The plan identifies measures that support development objectives while effectively addressing climate change through co-benefits.
- Core Components: The NAPCC consists of eight “National Missions,” which focus on climate change understanding, adaptation, mitigation, energy efficiency, and natural resource conservation.
Eight National Missions:
- National Solar Mission
- National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency
- National Mission on Sustainable Habitat
- National Water Mission
- National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem
- National Mission for a Green India
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture
- National Mission on Strategic Knowledge for Climate Change
Pyrocumulonimbus cloud
Why in News: The wildfires currently burning in the United States and Canada are so intense that they have generated ‘pyrocumulonimbus’ clouds, which can produce thunder and potentially ignite additional fires.
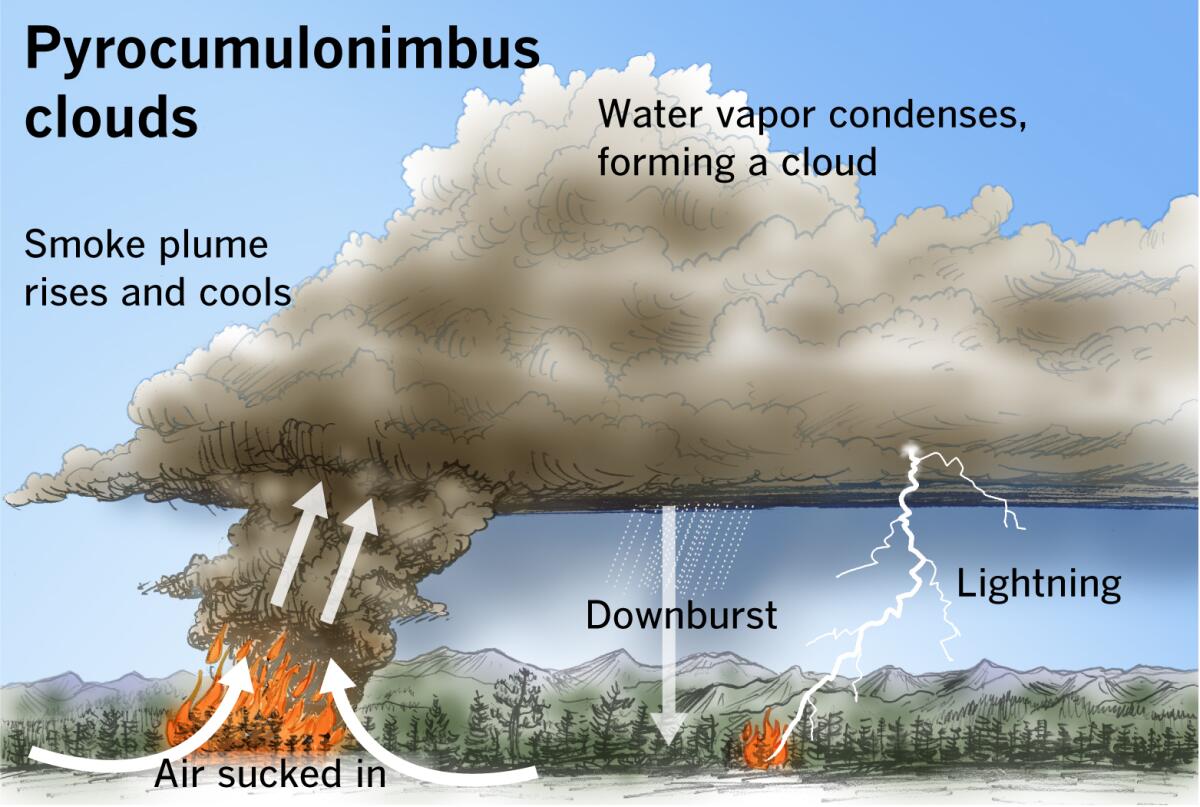
About Pyrocumulonimbus Clouds:
Occurrence:
- Pyrocumulonimbus clouds form during extremely intense wildfires.
- Volcanic eruptions can also lead to their formation.
Formation Process:
- Heat and Upward Movement: The intense heat from the wildfire heats the surrounding air, causing it to rise rapidly into the atmosphere.
- Cooling and Condensation: As this hot, buoyant air—laden with water vapor, smoke, and ash—ascends, it expands and cools.
- Formation of Pyrocumulus Cloud: When the air cools enough, water vapor condenses on ash particles, creating a grey or brown cloud known as a pyrocumulus cloud, or ‘fire cloud.’
- Development into Pyrocumulonimbus Cloud: If there is ample water vapor and the upward movement of hot air intensifies, the pyrocumulus cloud can develop into a pyrocumulonimbus cloud.
Characteristics:
- Altitude and Thunderstorms: These clouds can reach altitudes of up to 50,000 feet and are capable of generating their own thunderstorm systems.
- Lightning and Rain: While pyrocumulonimbus clouds can produce lightning, they generate little rainfall.
- Fire Spread: They can ignite new wildfires kilometers away from the main blaze and trigger strong winds that exacerbate the spread and unpredictability of the fire.
Impact of Climate Change:
- Contribution to Frequency: Scientists suggest that climate change may contribute to the increasing frequency of pyrocumulonimbus clouds.
- Rising Temperatures and Wildfires: Rising global temperatures are making wildfires more frequent and intense, leading to the more frequent formation of these clouds.
Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve
Why in News: The Chhattisgarh government announced on Wednesday that it will establish a new tiger reserve, which will be named the Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve.
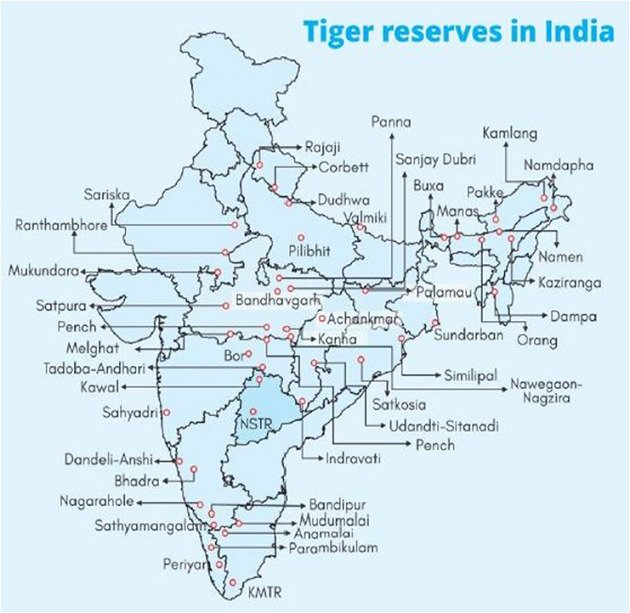
About Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Situated in the northern part of Chhattisgarh, bordering Madhya Pradesh and Jharkhand.
- Fourth Tiger Reserve: This reserve will be the fourth in Chhattisgarh, following Udanti-Sitanadi, Achanakmar, and Indravati Reserves.
- Area: The reserve spans the combined regions of Guru Ghasidas National Park and Tamor Pingla Wildlife Sanctuary in Chhattisgarh.
- Fauna: The area is home to a variety of mammal species, including tigers, leopards, hyenas, jackals, wolves, sloth bears, barking deer, chinkara, and chital.
- Rivers: It serves as the origin of major rivers such as Hasdeo, Gopad, and Baranga, and as a catchment area for rivers like Neur, Bijadhur, Banas, Rehand, and several smaller rivers and rivulets.
Guru Ghasidas National Park:
- Corridor Connectivity: The park connects Jharkhand and Madhya Pradesh, providing a corridor for tigers to move between the Bandhavgarh and Palamau Tiger Reserves.
- History: Originally part of the Sanjay Dubri National Park, Guru Ghasidas Park was established as a separate entity in Chhattisgarh’s Sarguja region after the state was formed in 2001.
Eta Carinae
Why in News: Astronomers are closely observing Eta Carinae, as it could be nearing a dramatic explosion.

About Eta Carinae:
Eta Carinae is an enormous star with a mass approximately 100 times that of our Sun.
Location:
- Situated about 7,500 light-years away in the Carina Nebula, Eta Carinae is one of the most massive and luminous stars known, making it a prime candidate for a supernova.
Historical Significance:
- Around 170 years ago, Eta Carinae experienced a major outburst, known as the Great Eruption, briefly becoming one of the brightest stars in the southern sky.
- This event led to the formation of the Homunculus Nebula, a distinctive hourglass-shaped cloud of gas and dust surrounding the star.
Unique Characteristics:
- Eta Carinae is the only known star to emit natural laser light, adding to its mysterious nature.
- Recent observations from the Hubble Space Telescope have revealed intricate details of the surrounding nebula, including unexplained diffraction spikes and radial streaks.
Future Supernova:
- Eta Carinae’s eventual explosion will be a monumental event, likely outshining any supernova observed in recent history, including SN 2006gy.
- This supernova will offer an extraordinary light show visible from Earth and provide invaluable insights into the life cycles of massive stars.



