Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Relevance: GS III- Sci & Tech
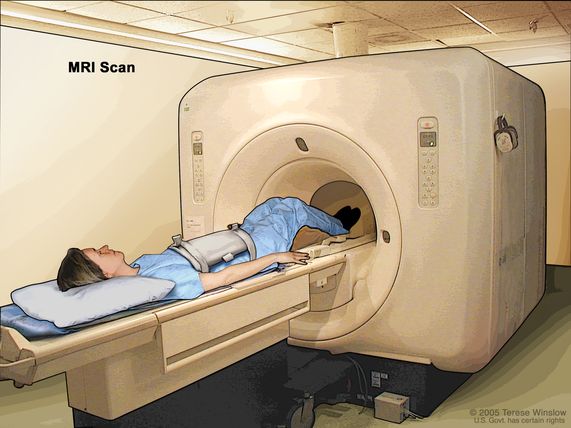
Why in News: Recently, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has garnered attention as an essential method for non-intrusive examination within the human body.
About MRI
- MRI is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure employed to capture images of soft tissues within the body.
- Soft tissue refers to any tissue that remains pliable without calcification, a process where calcium salts accumulate, causing hardening.
- It finds extensive application in imaging various body parts such as the brain, cardiovascular system, spinal cord, joints, muscles, liver, and arteries.
- Unlike X-rays, which rely on radiation, MRI scans utilize powerful magnets and radio waves to generate detailed images of soft tissues within the body.
- Professor Paul C. Lauterbur and Peter Mansfield were awarded the 2003 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their groundbreaking research leading to the development of MRI technology.
Working Principle of MRI:
- Hydrogen Atom Utilization: MRI procedures harness hydrogen atoms present in the scanned body part.
- MRI Machine Components: The MRI machine comprises four essential components, including a superconducting magnet, a radiofrequency pulse emitter, and a detector.
- Magnetic Field Application: The superconducting magnet generates a robust and steady magnetic field around the body, aligning the spin axes of hydrogen atoms either parallel or antiparallel to the field.
- Radiofrequency Pulse Emission: A radiofrequency pulse is emitted into the scanned body part, exciting only the small fraction of unpaired hydrogen atoms.
- Signal Detection and Image Formation: The emitted energy from the excited atoms is detected by a receiver and converted into signals.
- These signals are then utilized by a computer to produce two- or three-dimensional images of the scanned body part.
Importance of MRI:
- MRI plays a critical role in diagnosing and treating cancers such as prostate and rectal cancer, as well as monitoring neurological conditions like Alzheimer’s, dementia, epilepsy, and stroke.
- Furthermore, researchers employ MRI scans to investigate changes in blood flow, aiding in the understanding of brain activity, referred to as functional MRI.
Drip Pricing
Relevance: GS III- Economy

Why in News: The Center has recently cautioned against “drip pricing,” highlighting its potential to catch consumers off guard with undisclosed fees.
About Drip Pricing
- Definition: Drip pricing is a pricing strategy where businesses initially advertise only a portion of a product’s price and later reveal additional charges during the purchasing process.
- Types of Charges: Drip pricing often omits essential fees like booking, service, resort, or credit card fees, along with local hotel taxes, or extras such as internet access or specific amenities necessary for using the product or service.
- Method: These undisclosed costs are gradually disclosed to the buyer by the seller during the point of purchase, hence the term “drip pricing.”
- Usage: Commonly observed in sectors like hospitality, travel, and online payments, drip pricing aims to attract customers into starting the buying process, often making it inconvenient for them to restart their search upon discovering additional costs.
- Consumer Impact:
- Consumers generally prefer transparent pricing upfront and may feel deceived by later add-ons, leading to frustration.
- Drip pricing complicates comparison shopping and can disadvantage sellers who opt for more transparent pricing practices.
- Example: An instance of drip pricing is when the initial cost of an airplane ticket excludes baggage fees, which are revealed later in the purchasing process.
Rod Puppetry
Relevance: GS I- Art and Culture

Why in News: Recently, Padma Shri awardee Maguni Charan Kuanr passed away. He contributed to the arts by preserving the fading tradition of rod puppetry and promoting the traditional rod puppet dance.
About Rod Puppetry
Rod puppets, an evolution of glove puppets, are typically larger and controlled with rods from below. Today, this puppetry style is primarily found in West Bengal and Odisha.
Traditional Puppetry in West Bengal: The Putul Nautch
- Cultural Identity: In West Bengal, traditional puppets are known as Putul Nautch, crafted from wood and reflecting regional artistic styles.
- Evolution in Nadia District: In Nadia district, West Bengal, rod-puppets were once human-sized, akin to Japan’s Bunraku puppets, but this form is now nearly extinct.
- Surviving Form: The remaining Bengal rod-puppets stand at 3 to 4 feet in height, resembling actors from Jatra, a traditional theater form in the state.
- Design: These puppets typically have three joints, with the head and hands attached to rods. Manipulation involves a unique theatrical technique.
- Manipulation: Puppeteers wear a bamboo hub tied around their waist, supporting the rod holding the puppet, enabling synchronized movements.
- Performance Dynamics:
- Puppeteers stand behind a curtain, each handling a puppet, while dancing and moving to orchestrate corresponding puppet movements.
- They also sing and deliver stylized prose dialogues, accompanied by a group of musicians playing traditional instruments like drums, harmonium, and cymbals.
- Artistic Resonance: Both the music and verbal expressions bear resemblance to the Jatra theater, enhancing the cultural significance of the performance.
Distinctive Features of Odisha Rod Puppetry
In Odisha, rod puppetry deviates from other styles in several aspects.
- Size and Design: Rod puppets in Odisha are notably smaller, typically ranging from twelve to eighteen inches.
- Hybrid Design: These puppets typically have three joints, but unlike others, their hands are attached to strings rather than rods, blending elements of both rod and string puppetry.
- Manipulation Technique: Odisha rod-puppeteers sit on the ground behind a screen, employing a different manipulation technique compared to other regions.
- Verbal Expression: Unlike other forms, Odisha rod puppetry leans towards operatic verbal content, with impromptu prose dialogues being rare. Most dialogues are sung instead.
- Musical Fusion: The accompanying music in Odisha combines folk tunes with classical Odissi melodies, contributing to its distinct cultural flavor.
- Performance Structure: Performances typically begin with a short ritual orchestral piece called Stuti before the main play unfolds.
- Comparative Size and Style: Odisha’s puppets are smaller compared to those from Bengal or Andhra Pradesh, and the performance style tends towards operatic expressions rather than relying heavily on prose dialogues.
Yampuri: Bihar’s Traditional Rod Puppetry
- Artisanal Craftsmanship: In Bihar, the indigenous rod puppetry is known as Yampuri, crafted meticulously from wood.
- Unified Design: Unlike counterparts from West Bengal and Odisha, Yampuri puppets are singular pieces without any joints, presenting a distinct visual aesthetic.
- Unique Manipulation Technique: Manipulating Yampuri puppets demands exceptional skill due to their lack of joints, necessitating greater dexterity and finesse in performance.
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation Summit
Relevance: GS II- International Relations

Why in News: The Indian Foreign Minister recently participated in the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Summit held in Astana, Kazakhstan.
About Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
- Formation: The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is an enduring international organization formed in June 2001 in Shanghai, China.
- Purpose: Initially established as the Shanghai Five in 1996, it comprised Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Tajikistan, focusing on regional security, border troop reductions, and counterterrorism in the post-Soviet era.
- Expansion and Principles: In 2001, Uzbekistan joined the group, leading to its reformation as the SCO, enshrined by a charter embodying the principles of the “Shanghai Spirit” fostering cooperation.
- Global Representation: The SCO encompasses approximately 42% of the world’s population, spans 22% of its land area, and contributes about 20% to global GDP.
- Operational Details
- Officially, the working languages of the SCO are Chinese and Russian.
- The SCO Secretariat is located in Beijing, China.
Category | Countries |
Member States (8) | 🌍 China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, India, Pakistan |
India and Pakistan joined in 2017 🇮🇳🇵🇰 | |
Iran expected to join in 2023 🇮🇷 and Belarus in 2024 | |
Observer Members (4) | 🔍 Afghanistan, Belarus, Iran, Mongolia |
Iran’s procedure started in 2021 🇮🇷 | |
Belarus’s procedure started in 2022 🇧🇾 | |
Dialogue Partners (9) | 💬 Azerbaijan, Armenia, Egypt, Cambodia, Qatar, Nepal, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, Sri Lanka |
Procedure initiated for Bahrain, Kuwait, Maldives, Myanmar, UAE in 2022 🌐 |
Why is the SCO Significant?
- Security Focus with Asian Membership
- Security Issues: The SCO is one of the few international organisations that deal with security issues and primarily includes Asian members.
- Alternative Order: Regional heavyweights Russia and China emphasize the SCO as an alternative to the “Western” international order.
- Strategic Positioning Against US Influence
- BRICS Alliance: Along with the BRICS grouping, which includes India, South Africa, and Brazil, Russia and China are seen as positioning themselves against US influence.
- China-Russia Dynamics: Despite declarations of a “limitless friendship” between China and Russia, there is competition over who wields greater influence within the SCO.
- Central Asian Influence
- Russia’s Sphere: Central Asian republics have traditionally been viewed as part of Russia’s sphere of influence.
- China’s Leverage: China has sought to leverage the oil and gas-rich nations through investments in massive infrastructure projects, part of its larger Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- Inclusion of India and Pakistan
- 2017 Membership: India and Pakistan joined the SCO in 2017.
- Strategic Support: Russia supported India’s entry as a longstanding strategic partner, while China backed Pakistan to prevent a power imbalance favoring Russia.
- Context of US-Russia and US-China Relations
- US Tensions: The SCO’s expansion is influenced by deteriorating US ties with Russia and China.
- Recent Events: The 2022 Russia-Ukraine War and trade tensions with China under US President Donald Trump have spurred the inclusion of more countries in the SCO.
- Iran’s Inclusion
- Strategic Move: In 2023, Chinese state media Global Times noted that Iran’s inclusion was seen as enhancing the SCO’s international status and influence and breaking the US diplomatic blockade.
What Relevance Does the SCO Hold for India?
- Enhancing Cooperation with Central Asia
- Forum for Engagement: SCO membership allows India to enhance cooperation with Central Asian countries, with which it has not had particularly close relations since their formation in 1991.
- Security Communication: It enables India to maintain communication with major regional actors on common security issues.
- Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS)
- Counter-Terrorism Exercises: RATS assists members in preparing and staging counter-terrorism exercises.
- Intelligence Analysis: It analyzes key intelligence information from member states.
- Information Sharing: RATS shares information on terrorist movements and drug trafficking.
- Managing Ties Among Partners
- Tense Relationships: The relevance of the SCO is questioned due to difficulties in managing ties among partners, especially given India’s tense relationships with China and Pakistan.
- Virtual Summit: Last year, India decided to hold a virtual summit instead of an in-person one during its presidency.
- India’s Position on BRI
- New Delhi Declaration: India refused to sign off on a paragraph supporting the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in the New Delhi Declaration.
- Opposition to CPEC: India’s opposition stems from the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), part of the BRI, which is proposed to pass through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, seen by India as a violation of its territorial integrity and sovereignty.
Implementing the Street Vendors Act
Relevance: GS II : Polity
![]()
Context: Ten years have passed since the enactment of the Street Vendors (Protection of Livelihood and Regulation of Street Vending) Act on May 1, 2014.
Acknowledging Street Vendors in India:
The legislation acknowledges the diverse contributions of street vendors, constituting approximately 2.5% of urban populations across cities.
- Role : Street vendors play a crucial role as providers of daily necessities, forming integral links in the food, nutrition, and goods distribution network while maintaining affordability.
- Importance of Street Vendors: Vending serves as a vital income source for many migrants and impoverished urban dwellers, offering a steady albeit modest means of livelihood.
- Cultural Significance: Street vendors not only sustain livelihoods but also enrich India’s cultural tapestry. Iconic street foods like Mumbai’s vada pav and Chennai’s roadside dosai epitomize their cultural significance and heritage.
Street Vendors (Protection of Livelihood and Regulation of Street Vending) Act, 2014:
The legislation was crafted to acknowledge and regulate street vending in urban areas, with the goal of safeguarding and regulating this aspect of urban life through State-level regulations and programs, administered by Urban Local Bodies (ULBs).
- Defining Responsibilities: It clearly outlines the duties of vendors and different tiers of government, emphasizing the positive urban contribution of vendors and the crucial need to protect their livelihoods.
- Certification: A notable provision is the commitment to integrating all existing vendors into designated vending zones and issuing them vending certificates.
- Establishment of Inclusive Committees: The Act institutes participatory governance mechanisms like Town Vending Committees (TVCs), wherein 40% of members are comprised of street vendor representatives, with a mandated 33% representation from female vendors.
- Addressing Disputes: These committees are entrusted with ensuring the inclusion of all existing vendors in vending zones and providing avenues for resolving complaints and disagreements through the proposed Grievance Redressal Committee, led by a civil judge or judicial magistrate.
Challenges
- Escalating Harassment: Despite the Act’s intention to safeguard and regulate street vendors, there has been a noticeable increase in instances of harassment and forced removals.
- Outdated Bureaucratic Mindset: Much of this mistreatment originates from an antiquated bureaucratic perspective that views vendors as unlawful entities to be eradicated.
- Lack of Awareness: There exists a widespread deficiency in comprehension and awareness regarding the Act among state authorities, the public, and even the vendors themselves.
- Control Over TVCs: Town Vending Committees (TVCs) often remain under the dominance of local city authorities, with minimal involvement from street vendor representatives. Additionally, the representation of women vendors in TVCs tends to be tokenistic.
- Weak Urban Governance Mechanisms: Existing urban governance structures frequently lack robustness, failing to effectively integrate with the framework established by the 74th Constitutional Amendment Act.
- Limited Authority and Resources: Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) often operate without adequate authority and resources to implement the Act’s provisions effectively.
- Exclusionary Urban Ideals: Prevailing notions of achieving a ‘world-class city’ tend to exclude street vendors, portraying them as obstacles to urban advancement rather than recognizing their legitimate role in the urban economy.
Way Forward:
Initial Central Oversight:
- The Act’s success relies on robust support, which initially should come from the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- Top-down direction and management might be necessary in the beginning.
Decentralization for Effectiveness:
- Over time, oversight should shift to local levels to better cater to the diverse needs of street vendors nationwide.
- Decentralization ensures effectiveness in addressing varying contexts.
Empowering Street Vendors:
- Positive examples like PM SVANidhi, a micro-credit facility, showcase initiatives to empower street vendors.
Strengthening Local Capacities:
- ULBs’ capacities should be bolstered to effectively plan for street vending in cities.
- Transition from authoritative department-led actions to inclusive processes at the TVC level is crucial.
Policy Adaptation:
- Urban schemes, city planning guidelines, and policies should be revised to include provisions for street vending.
Addressing New Challenges:
- Climate change impacts, increased vendor numbers, competition from e-commerce, and reduced incomes pose new challenges.
- Broad welfare provisions of the Act must be creatively utilized to meet emerging needs.
Adaptation of National Urban Livelihood Mission:
- The Act’s sub-component on street vendors within the National Urban Livelihood Mission needs adaptation to address altered realities and innovate solutions.



