Tell Umm Amer Heritage site
Why in News: During its 46th session in New Delhi, the World Heritage Committee (WHC) decided to include the Palestinian site of Tell Umm Amer in both the UNESCO World Heritage Site List and the List of World Heritage in Danger.

About Tell Umm Amer Heritage Site
- Geography: Situated on the coastal dunes of the Nuseirat Municipality, approximately 10 km south of Gaza city.
- Founding: An ancient Christian monastery founded in the fourth century by Hilarion the Great (291-371 CE).
- Alternative Name: Also known as the ‘Monastery of Saint Hilarion.’
- Monastic Community: It was the first monastic community in the Holy Land, setting the stage for the spread of monastic practices in the region.
- Strategic Position: Occupied a strategic location at the crossroads of major trade and communication routes between Asia and Africa.
UNESCO
- Full Form: United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization.
- Specialized Agency: Part of the United Nations (UN).
- Constitution: Entered into force in 1946, focusing on promoting international collaboration in education, science, and culture.
- Headquarters: Permanent headquarters are located in Paris, France.
- Parent Organization: United Nations Economic and Social Council.
- Peace and Security: Contributing to peace and security by promoting collaboration among nations through education, science, and culture.
- Sustainable Development: Promoting sustainable development and intercultural dialogue.
- Beliefs: UNESCO believes that these areas are crucial for building a more just, peaceful, and inclusive world.
Indexation
Why in News: One of the most contentious decisions announced in the Union Budget for 2024-25 is the change in the long-term capital gains (LTCG) tax regime, especially the withdrawal of the indexation benefit.

Indexation
Definition:
- Process: Indexation is the process of adjusting the original purchase price of an asset or investment to account for inflation.
- Purpose: It neutralizes the impact of inflation on the asset’s value over time.
Function:
- Inflation Adjustment: Inflation reduces the value of money over time. Indexation helps in determining the cost of acquisition by factoring in the inflation during the holding period.
- Indexed Cost of Acquisition: The adjusted cost of acquisition, known as the indexed cost of acquisition, is used to calculate gains or losses when the asset is sold or the investment is redeemed.
- Realistic Returns: Returns calculated on the indexed cost of acquisition are generally more realistic than absolute gains based on the actual purchase price.
Benefits:
- Tax Efficiency: Indexation is an effective way to reduce the tax burden on returns from investments.
- Applicability: It is applicable to long-term investments, including debt funds and other asset classes. Indexation adjusts the purchase price of these investments.
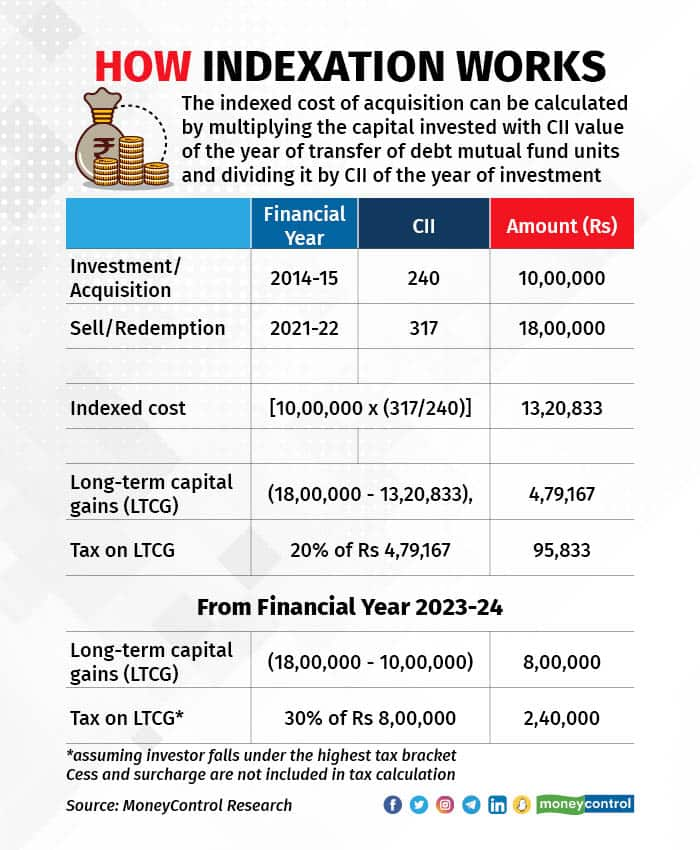
Capital Gains Tax
- Nature: Capital gains tax is a tax imposed on the profit from the sale of an asset.
- Calculation: It is calculated as the difference between the sale price and the purchase price of the property or asset.
- Property Sales: Any gain or loss from the sale of a house property may be subject to capital gains tax.
- Types of Capital Gains:
- Short-term Capital Gains: Gains from assets held for a short period.
- Long-term Capital Gains: Gains from assets held for a longer period.
Importance:
- Tax Head: Gains or losses from the sale of assets are categorized under the ‘Capital Gains’ head for tax purposes.
- Impact on Investments: Understanding capital gains tax is crucial for effective financial planning and investment strategies.
Notified Disaster
Why in News: Recently, the Minister of State for the Union Ministry of Science and Technology informed Lok Sabha that the 15th Finance Commission declined to add heatwaves to the notified disaster list.
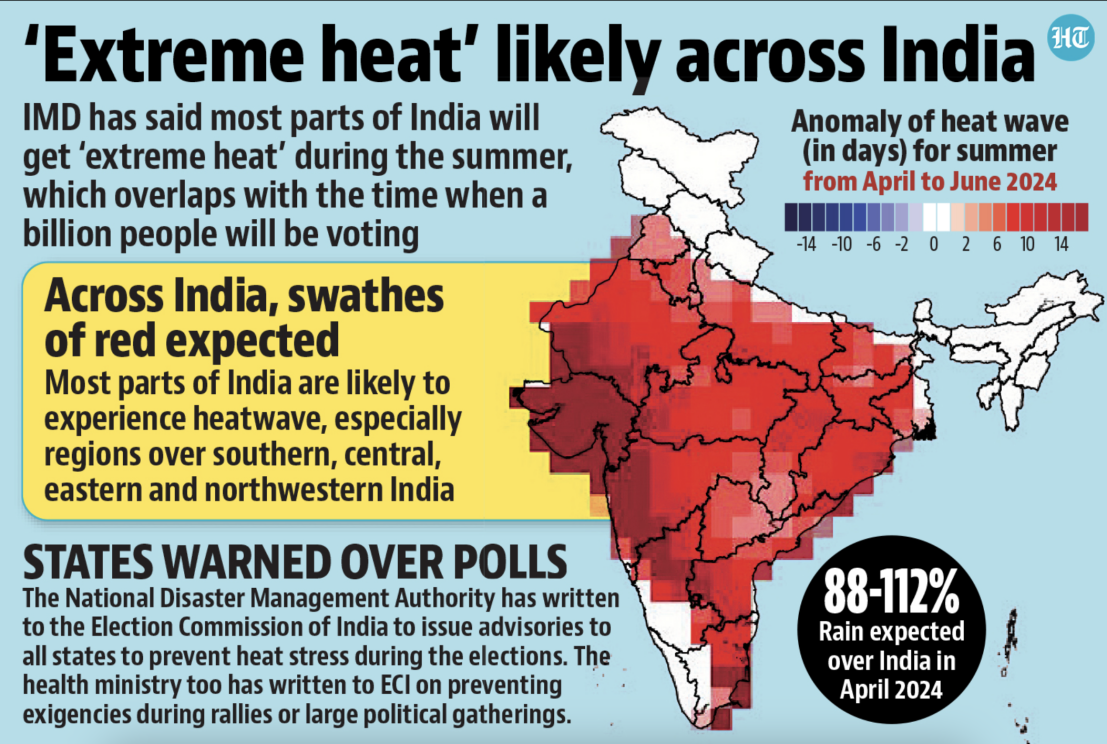
About Notified Disasters in India
Definition:
- Disaster Management Act, 2005: Defines a disaster as a “catastrophe, mishap, calamity or grave occurrence” resulting from natural or man-made causes that leads to substantial loss of life, property destruction, or environmental damage.
- Notified Disasters:
India has classified 12 disasters as Notified Disasters eligible for assistance from the National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF) and State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF):
- Cyclone
- Drought
- Earthquake
- Fire
- Flood
- Tsunami
- Hailstorm
- Landslide
- Avalanche
- Cloud Burst
- Pest Attack
- Frost and Cold Wave
Heat Waves
- Heat Wave Declaration: The India Meteorological Department (IMD) declares a heatwave based on specific temperature criteria:
- Plains: Temperature exceeds 40°C.
- Coastal Areas: Temperature exceeds 37°C.
- Hills: Temperature exceeds 30°C.
National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
Role and Functions:
- Policy Formulation: NDMA is responsible for laying down policies, plans, and guidelines for disaster management in India.
- Mitigation Efforts: It aims to promote a national resolve to mitigate damage and destruction caused by natural and man-made disasters.
- Collective Efforts: NDMA focuses on sustained and collective efforts to reduce disaster impact.
Key Facts:
- Objective: To enhance disaster preparedness and response capabilities.
- Guidelines: Provides a framework for coordinated and effective disaster management at national, state, and local levels.
- Awareness and Training: Conducts awareness campaigns and training programs to equip communities and responders with the necessary skills and knowledge for disaster management.
E-Upahaar Portal
Why in News: Rashtrapati Bhavan will auction selected gift items presented to the President and former Presidents on various occasions via an online portal called E-Upahaar.

About E-Upahaar Portal
- Purpose: An auction portal of the President’s Secretariat (office of the President of India), Rashtrapati Bhavan for auctioning gift items presented to the Hon’ble President and former Presidents of India.
- Launch: Launched by the President of India on July 25, 2024.
- Development: Conceptualized, designed, developed, and hosted by the National Informatics Centre (NIC), Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- Objective: Aims to increase citizen engagement and support noble causes, with all auction proceeds donated to help children in need.
Key Facts about the National Informatics Centre (NIC)
- Establishment: Founded in 1976 to provide technology-driven solutions to Central and State Governments.
- Affiliation: Operates under the Union Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- Focus: Provides e-Government solutions and support to various government departments.
- Network: Through its ICT Network, “NICNET,” maintains institutional linkages with all Central Government Ministries/Departments and 36 State Governments/Union Territories across India.
- Major Activities:
- Setting up ICT Infrastructure
- Implementing National and State Level e-Governance Projects/Products
- Providing consultancy to government departments
- Conducting Research & Development



