Eturnagaram Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in News: A rare weather event—the collision of two cyclones—has been identified as the cause of the destruction of thousands of trees in the Eturnagaram wildlife sanctuary located in the Mulugu district.

About Eturnagaram Wildlife Sanctuary
Location
- Geographical Position: Eturnagaram Wildlife Sanctuary is situated near the borders of Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, and Telangana in the tribal village of Eturnagaram, Mulugu district, Telangana.
- Establishment: It was designated as a wildlife sanctuary in 1952 by the Hyderabad Nizam Government.
River
- Water Sources: The Dayyam Vagu river serves as a water source, dividing the sanctuary into two sections.
- Additional Rivers: The Godavari River also flows through the sanctuary.
Flora
- Vegetation: The sanctuary is densely covered with natural vegetation and is classified as tropical dry deciduous forest.
- Tree Species: It is abundant in teak, bamboo, and other tree species, including madhuca and terminalia.
Fauna
- Wildlife: The sanctuary is home to various species such as Tigers, Leopards, Panthers, Wolves, Wild Dogs, Jackals, Sloth Bears, Chousingha, Black Bucks, Nilgai, Sambars, Spotted Deer, and Four-Horned Antelopes.
- Reptiles: The sanctuary features diverse aquatic life, including Mugger crocodiles and snakes like Cobras, Pythons, and Kraits.
Cultural Significance
Temples: The well-known Sammakka-Saralamma Temple is located within the sanctuary.
Source: TH
Taiwan Strait
Why in News: For the first time, a Japanese warship sailed through the Taiwan Strait to demonstrate its commitment to freedom of navigation.
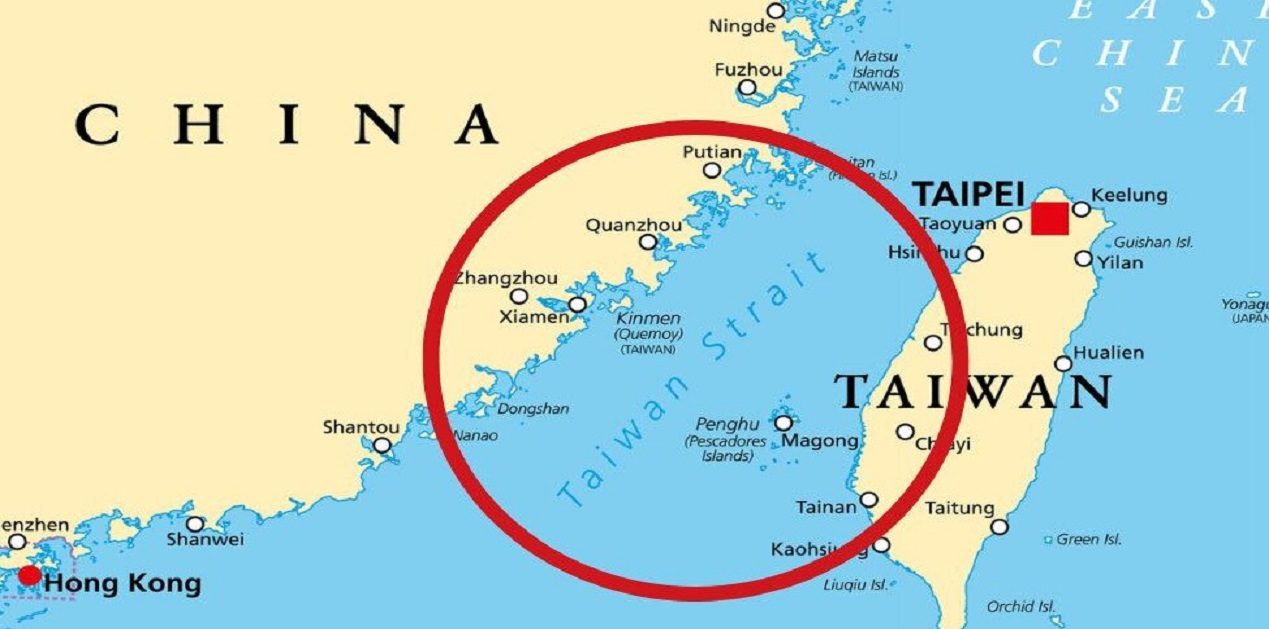
About Taiwan Strait
- Alternate Name: The Taiwan Strait is also referred to as the Formosa Strait, separating the island of Taiwan from continental Asia.
- Major Ports: Key ports in the region include Amoy in mainland China and Kao-hsiung in Taiwan.
- Draining Rivers: Several rivers, such as the Jiulong and Min rivers from China’s Fujian Province, flow into the Taiwan Strait.
- Significant Islands: The largest islands on the Taiwan side include Penghu (or Pescadores), Xiamen, and Pingtan.
Strategic Importance
- Corridor: The Taiwan Strait serves as a vital corridor connecting the South China Sea to the East China Sea. It is a heavily trafficked waterway, facilitating the transportation of millions of tons of cargo each year.
- Fishing Grounds: It is one of the most important fishing areas in China, home to over a hundred economically significant fish species.
What is a Strait?
- A strait is a narrow body of water that links two larger bodies of water.
- Natural vs. Man-Made: Unlike a canal, which is artificially constructed through an isthmus (a narrow strip of land), a strait is naturally formed.
- Significance: Straits are crucial transportation routes, enabling ships to navigate between different bodies of water.
Source: TH
Asia Power Index
Why in News: India secured the third position in the annual Asia Power Index published by an Australian think tank.

About Asia Power Index
Launched by the Lowy Institute in 2018, the Asia Power Index is an annual assessment of power dynamics in the Asia-Pacific region.
- Scope of Evaluation
- Coverage: The Index evaluates 27 countries in the Asia-Pacific, analyzing their capacity to influence and respond to external environments.
- Focus: It emphasizes both the material capabilities of states and their influence on the international stage.
2024 Edition Highlights
- Comprehensive Assessment: The 2024 edition provides one of the most thorough evaluations of power distribution in the region to date.
- New Inclusion: Timor-Leste has been included for the first time, highlighting its increasing significance in Southeast Asia.
Resource-Based Determinants
- Economic Capability: Assesses a country’s economic strength using indicators such as GDP at purchasing power parity (PPP), technological advancement, and global economic connectivity.
- Military Capability: Evaluates conventional military strength based on defense spending, armed forces size, weapon systems, and capabilities like long-range power projection.
- Resilience: Measures the internal capacity to prevent threats to state stability, considering institutional strength, geopolitical security, and resource availability.
- Future Resources: Projects the future distribution of resources, including economic, military, and demographic factors expected by 2035.
Influence-Based Determinants
- Economic Relationships: The ability to exert leverage through trade, investment, and economic diplomacy.
- Defense Networks: Strength of alliances and partnerships, assessed through military cooperation and arms transfers.
- Diplomatic Influence: Extent of diplomatic reach, participation in multilateral forums, and ambition in foreign policy.
- Cultural Influence: Capacity to shape global public opinion through cultural exports, media, and people-to-people connections.
- Calculation: A country’s overall power score is derived from a weighted average of these eight determinants, encompassing a total of 131 individual indicators.
Source: ET
MAPCIS Crater
Why in News: Recently, Australian researchers discovered a massive impact crater known as MAPCIS, which has the potential to transform our understanding of Earth’s geological history.

About MAPCIS Crater
- Classification: The MAPCIS crater is categorized as a nonconcentric complex crater and may offer valuable insights into Earth’s geological and biological evolution.
- Size: It stretches an impressive 600 kilometers across central Australia.
- Name: The structure is officially named the Massive Australian Precambrian-Cambrian Impact Structure (MAPCIS).
- Impact Timing: The impact that formed the crater is believed to have occurred at the end of the Ediacaran period.
- Geological Features: The crater features significant deposits of pseudotachylite breccia (melt rock) at its center, shocked minerals such as lonsdaleite (a type of shocked diamond), and elevated levels of iridium typically associated with impact events.
Key Facts About the Ediacaran Period
- Timeframe: The Ediacaran Period spans from 635 to 541 million years ago.
- Geological Context: It represents the uppermost division of the Proterozoic Eon during Precambrian time and is the latest of the three periods in the Neoproterozoic Era.
- Biological Significance: This period is notable for producing some of the earliest known evidence of multicellular animal evolution.
- Geological and Biological Change: The Ediacaran was marked by significant geological and biological transformations, reflecting the transition from a planet dominated by microscopic life to one bustling with diverse animal forms during the Cambrian period.
Source: BT



