Carbon Budget |
Why in News: The Minister of State for Environment conveyed to the Rajya Sabha that developed nations have consumed more than 80% of the global carbon budget, thereby restricting the available carbon quota for countries such as India in the future.
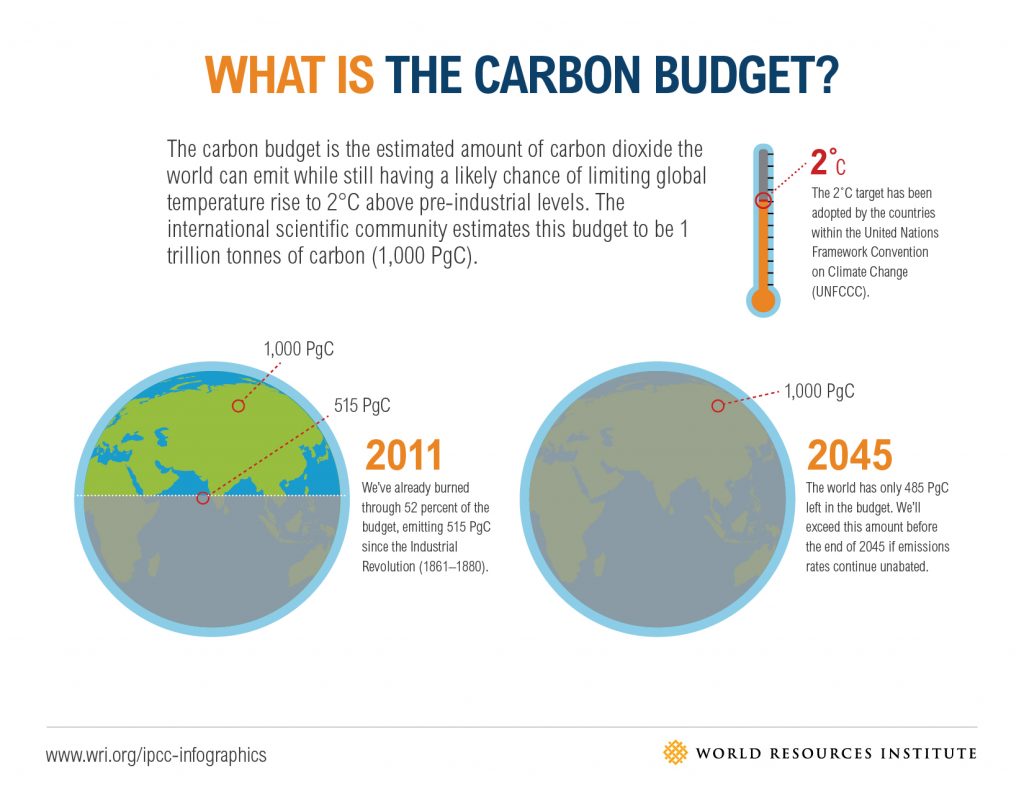
About Carbon Budget:
- Definition: The carbon budget refers to the quantity of greenhouse gases that humanity can emit while still having a chance to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius compared to pre-industrial levels, as stipulated by the Paris Agreement.
- Mechanism: It functions by establishing a cap on the total amount of CO2 emissions permitted over a specific timeframe.
India and Carbon Budget:
- Emission Comparison: India’s annual emissions are significantly lower than those of the top three emitters, namely China, the US, and the European Union. India’s contribution to global cumulative emissions from 1850 to 2019 is less than 4%.
- India’s INDC Goals:India’s Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDC) aim to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius by reducing emissions intensity of GDP by 45% by 2030 (compared to 2005 levels) and achieving 50% cumulative electric power capacity from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030.
Inclusive Conservation Initiative |
Why in News: A recent report outlining the initial stage of implementation of the Inclusive Conservation Initiative (ICI) was published.
.png)
About Inclusive Conservation Initiative (ICI):
- Global Scope:The ICI is a worldwide endeavor aimed at providing assistance to Indigenous Peoples and Local Communities (IPLCs) in safeguarding and managing their lands, territories, and resources, which are abundant in biodiversity and ecosystems.
- Respect for Rights and Cultures:It acknowledges and honors the rights, cultures, knowledge, practices, and governance systems of IPLCs as crucial components for achieving effective and fair conservation outcomes.
- Funding and Implementation: The ICI is financially supported by the Global Environment Facility (GEF) and executed through a collaboration between Conservation International (CI) and the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as joint GEF Implementing Agencies.
Global Biodiversity Framework Fund |
Why in News: At the Seventh Assembly of the Global Environment Facility (GEF), the Global Biodiversity Framework Fund (GBFF) was recently approved.

About Global Biodiversity Framework Fund (GBFF):
- Purpose:Established to facilitate the implementation of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF), GBFF endeavors to promote the conservation and sustainability of wildlife and ecosystems.
- Investment Mobilization: GBFF is tasked with mobilizing and expediting investment from governments, philanthropic organizations, and the private sector.
- Indigenous Support: Up to 20% of the total funds will be allocated to assist Indigenous-led initiatives aimed at preserving and conserving biodiversity.
- Assistance for Vulnerable Regions: Small Island Developing States and Least Developed Countries will receive more than one-third of the fund’s resources to aid in their conservation efforts.
Carbon Registry |
Why in News: The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) has created open-source software enabling countries to efficiently oversee national data and procedures for carbon credit trading.
National Carbon Registry:
Adaptability: Recognized as a digital public good (DPG), this digital platform is accessible for countries to utilize and customize according to their particular requirements. Its primary purpose is to streamline the monitoring and administration of carbon credits.
State of the Climate in Asia 2023: WMO |
Why in News: According to the latest ‘State of the Climate in Asia 2023’ report from the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), Asia stands out as the most disaster-prone region globally.
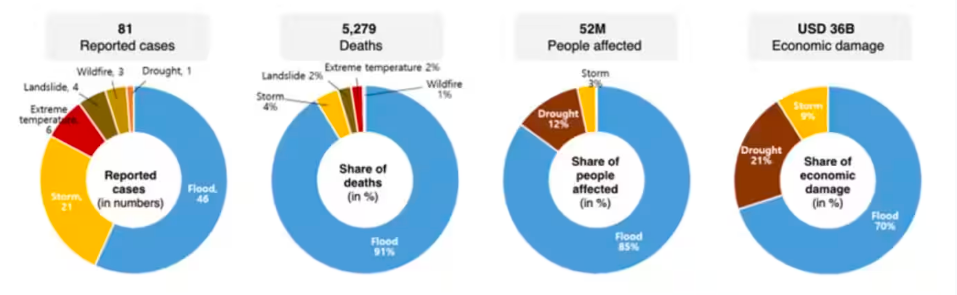
About the ‘State of the Climate in Asia 2023’ Report:
- Collaborative Effort: This report is a joint endeavor involving National Meteorological and Hydrological Services (NMHSs) in the region, the UN Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP), the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), and other specialized agencies of the United Nations.
- Third Edition: The 2023 report marks the third installment in the series.
Climate Smart Agriculture |
Why in News: The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is embarking on a significant endeavor to transform desert areas into fertile farmland using climate-smart agricultural practices.
About Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA):
- Definition:Climate-smart agriculture (CSA) is a holistic approach to landscape management encompassing cropland, livestock, forests, and fisheries, aimed at addressing the interconnected challenges of food security and climate change.
- Climate Smart Agricultural Practices:
- Crop Management:Involves practices such as intercropping, crop rotations with legumes, utilizing drought, wind, and flood-tolerant crop varieties, composting, mulching, and adopting organic fertilizers.
- Livestock Management:Encompasses improved feeding strategies, rotational grazing, using suitable crops as animal feed, and enhancing livestock health and husbandry.
- Agroforestry: Includes strategies like planting trees for windbreaks, utilizing nitrogen-fixing trees, and integrating fruit orchards into agricultural landscapes.
- Integrated Food Energy Systems:Involves the implementation of biogas technology, improved stoves, solar power, and gravity-fed irrigation systems.
Climate Financing |
Why in News: France recently organized a summit for a New Global Financing Pact to tackle contentious matters concerning climate financing.
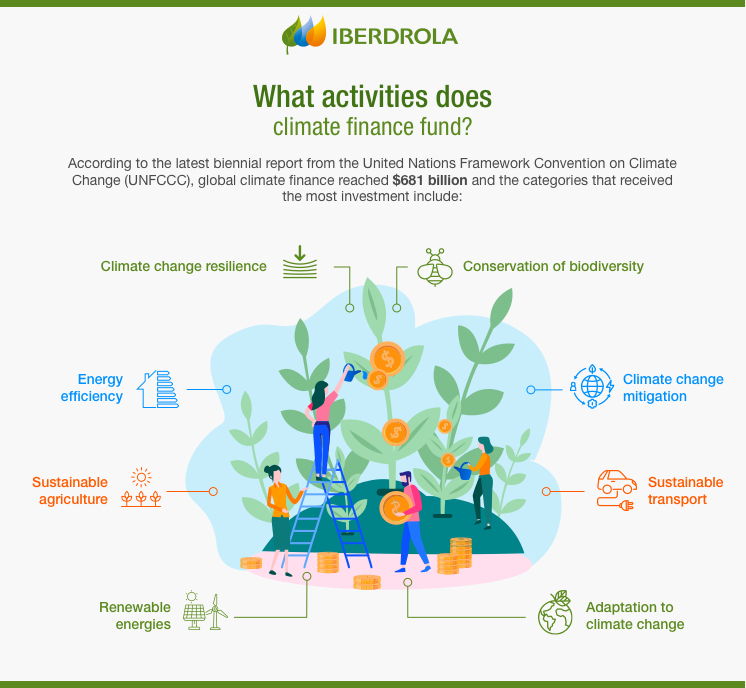
About Climate Financing:
- Definition:Climate financing refers to funding sources intended to support actions aimed at mitigating and adapting to climate change.
- Objective: The focus is on evaluating “all the means and ways of increasing financial solidarity with the South.”
- Four Main Objectives:
- Restore Fiscal Space: Ensure that countries facing short-term challenges have the necessary financial capacity.
- Foster Private Sector Development:Promote the growth of the private sector in low-income countries.
- Encourage Investment in Green Infrastructure: Stimulate investment in environmentally friendly infrastructure for the energy transition in emerging and developing nations.
- Mobilize Innovative Financing: Secure innovative financing options for countries vulnerable to climate change.




