Nagorno-Karabakh Region
Why in News: Russian peacekeeping forces have initiated their withdrawal from Nagorno-Karabakh subsequent to Azerbaijan’s reclaiming of the contested region from Armenian separatists in the previous year.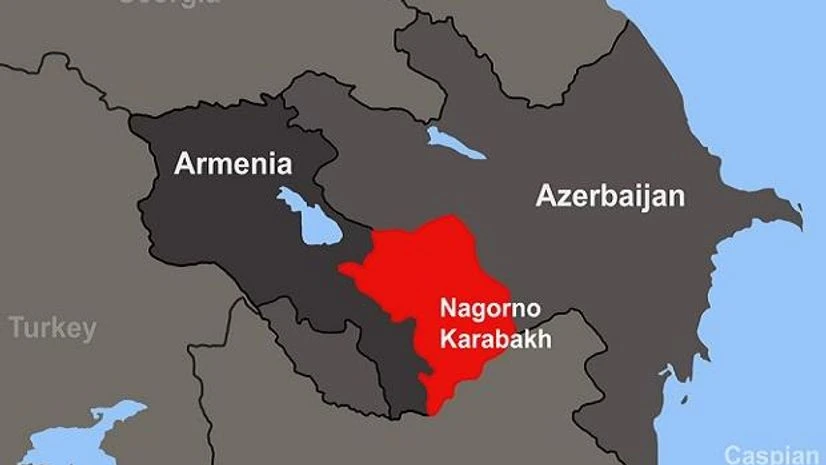)
About Nagorno-Karabakh Region:
- Nagorno-Karabakh, referred to as Artsakh by Armenians, is a mountainous enclave situated in the South Caucasus region.
- It has been a point of contention since the dissolution of the Russian Empire in 1917, with both Azerbaijan and Armenia laying claim to the territory.
- Despite being internationally recognized as part of Azerbaijan, Nagorno-Karabakh’s population is predominantly ethnic Armenians, governing themselves with close ties to Armenia, albeit lacking official recognition from it and other UN member states.
- Armenians, predominantly Christian, assert historical dominance in the region dating back centuries, while Azerbaijan, with a mostly Muslim population, also stakes its historical identity to the area.
History of Nagorno-Karabakh:
- Throughout history, the enclave has been under the influence of various powers, including Persians, Turks, Russians, Ottomans, and Soviets.
- After the Russian Revolution, Armenia and Azerbaijan engaged in conflict over the region.
- With Bolshevik control established in Azerbaijan, Armenia aligned itself with Bolsheviks, leading to the Sovietization of the Caucasus.
- Nagorno-Karabakh remained part of the Azeri Soviet Socialist Republic but with autonomous status, known as the “Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast.”
- During the collapse of the Soviet Union, the First Nagorno-Karabakh War (1988-1994) erupted between Armenians and Azerbaijanis, resulting in Azerbaijan losing control over a significant portion of its territory, leaving Armenians in charge of most of Karabakh and additional surrounding areas.
Source: TH
Vasuki Indicus
Why in News: Recently, researchers announced the finding of fossils belonging to one of the largest snakes known to have existed, which they have named Vasuki Indicus.
About Vasuki Indicus
- Discovery Location: The fossils of Vasuki Indicus were discovered in Kutch, Gujarat, India.
- Mythological Inspiration: The name “Vasuki” is derived from the mythical snake often depicted around the neck of the Hindu god Shiva.
- Historical Period: Vasuki Indicus lived during the Middle Eocene period, approximately 47 million years ago, in India.
- Environmental Conditions: It thrived in relatively warm temperatures, estimated to be around 28°C during its time of existence.
Taxonomic Classification:
- Belonging to the extinct Madtsoiidae snake family, Vasuki Indicus represents a unique lineage from India.
- Madtsoiidae snakes were terrestrial creatures that existed from the Upper Cretaceous to the Late Pleistocene period.
Geographic Spread: Originating in India, Madtsoiidae snakes spread through southern Eurasia and into North Africa after the collision of the Indian subcontinent with Eurasia.
Physical Characteristics:
- Vasuki Indicus reached lengths of 10 to 15 meters and weighed approximately 1 tonne.
- It likely had a broad and cylindrical body, resembling Titanoboa, one of the longest known snakes in history.
- As a slow-moving ambush predator, Vasuki Indicus subdued its prey through constriction, similar to anacondas and pythons.
Source: TH
Salas y Gómez
Why in News: Scientists recently unveiled the identification of 160 marine species following an expedition to explore the Salas y Gómez area.
Location and Orientation:
- Salas y Gómez is an underwater mountain chain found in the Southeastern Pacific Ocean.
- It extends in a west-east direction, with its western tip intersecting the East Pacific Rise within Chile’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of the Easter Islands, while its eastern end connects with the western part of the Nazca Ridge.
Ecosystem Isolation:
- The region’s ecosystems are secluded due to the presence of the Atacama Trench, the Humboldt Current System, and an extremely low oxygen zone.
Jurisdiction and Boundaries:
- Most of the waters surrounding Salas y Gómez and Nazca ridges are in areas beyond national jurisdiction (ABNJ).
- Smaller portions fall under the national waters of Chile and Peru.
Biodiversity:
- This area is home to unique biodiversity, boasting some of the highest levels of marine species found nowhere else on the planet.
Marine Protected Area Consideration:
- It is among the global sites being considered for designation as a high seas marine protected area, contingent upon the ratification of the UN High Seas Treaty.
Source: IE
Ethylene Oxide
Why in News: The Center for Food Safety in Hong Kong has issued a recall for Everest Fish Curry Masala, originating from India, citing the detection of ethylene oxide pesticide levels that surpass the allowable limit.
About Ethylene Oxide
Physical Properties:
- Ethylene oxide is a flammable gas with a slightly sweet scent that readily dissolves in water.
- It presents itself as a transparent, colorless gas with a faint ethereal odor.
Manufacturing and Usage:
- Ethylene oxide is a synthetic chemical primarily utilized in the production of ethylene glycol.
Applications:
- A small proportion, less than 1%, is employed to manage insects in select stored agricultural goods.
- Hospitals utilize minute quantities for sterilizing medical equipment and supplies.
Health Effects:
- Ethylene oxide exposure primarily affects the human central nervous system, leading to depression, and can cause irritation to the eyes and mucous membranes.
- Chronic exposure may result in eye, skin, nose, throat, and lung irritation, along with potential damage to the brain and nervous system.
Source: TH



