Europa Clipper Mission
Why in News: NASA is preparing to launch the Europa Clipper mission, which is designed to investigate Europa, one of Jupiter’s icy moons.

About Europa Clipper Mission
- Objective: The Europa Clipper mission is a NASA initiative to investigate Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa.
- Mission Approach: A spacecraft will be placed in orbit around Jupiter to conduct a thorough study of Europa.
- Significance: It is the first NASA spacecraft dedicated to exploring an ocean world beyond Earth, aiming to determine if Europa could potentially be habitable.
- Evidence of Water: Europa is believed to have a subsurface ocean of liquid water beneath its icy crust.
- Spacecraft Dimensions: The spacecraft measures 100 feet (30.5 meters) in length and about 58 feet (17.6 meters) in width, making it the largest NASA spacecraft developed for a planetary mission.
- Mission Design: Europa Clipper will orbit Jupiter and perform 49 close flybys of Europa to gather essential data on potential habitats beneath its frozen surface.
- Scientific Equipment: The spacecraft is equipped with nine scientific instruments and a gravity experiment that utilizes its telecommunications system.
- Data Collection: All scientific instruments will operate simultaneously during each flyby to ensure comprehensive data collection, which will be layered to provide a complete analysis of the moon.
- Power Supply: The spacecraft features large solar arrays to harness sufficient sunlight for its power requirements while operating in the Jupiter system.
Square Kilometer Array Telescope
Why in News: The Square Kilometer Array (SKA), the largest radio telescope under construction globally, has successfully conducted its first observations, indicating that a portion of the facility is now operational despite being incomplete.

About Square Kilometer Array Telescope
The Square Kilometer Array (SKA) is an advanced international facility designed to create the world’s largest and most sensitive radio telescope, aimed at addressing various cutting-edge scientific objectives.
Location:
- The SKA is split between two sites: SKA-Low in Australia and SKA-Mid in South Africa, with operational headquarters located in the UK. This arrangement is anticipated to transform radio astronomy.
Components:
- SKA-Low will consist of 131,072 antennas, each standing two meters tall, while SKA-Mid will feature 197 large parabolic dish antennas.
- SKA-Low operates in the frequency range of 50 to 350 MHz, whereas SKA-Mid operates in the 350 MHz to 15.4 GHz band.
Scientific Goals:
- The facility is designed to observe the universe in innovative ways, tackling questions regarding the origins of the universe, the formation and evolution of galaxies, and the search for the origins of life.
International Collaboration:
- India joined the SKA project in December 2022, joining other participating countries including Canada, China, Italy, New Zealand, Sweden, and the Netherlands.
Pheromone
Why in News: Recently, Indian scientists have created a sustainable pheromone dispenser that features a controlled release rate, which has the potential to reduce pest control and management costs.
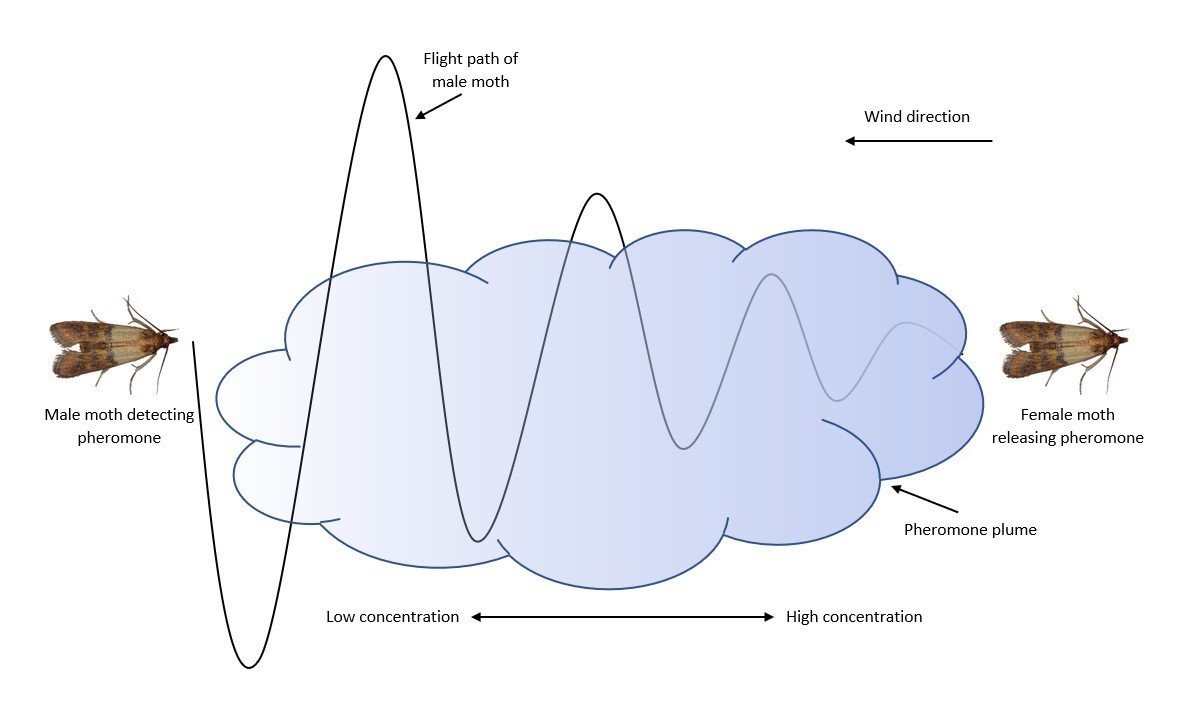
About Pheromones
- Definition: Pheromones are chemical substances secreted by an individual and detected by another of the same species.
- Presence: Found in all bodily secretions, particularly in axillary sweat, and are detected by the olfactory system.
- Type: Classified as ecto-hormones, as they are released outside the body.
Types of Pheromones
- Releaser Pheromones: Trigger immediate responses in other individuals.
- Signaler Pheromones: Convey information about the individual releasing them, such as helping a mother recognize her baby.
- Modulator Pheromones: Influence mood and emotions.
- Primer Pheromones: Affect hormonal changes, notably during pregnancy or menstrual cycles.
Animal Behavior
Animals use pheromones to initiate various behaviors, including:
- Raising alarms
- Signaling food trails
- Warning off threats
- Bonding with offspring
Amazon River
Why in News: The Amazon River basin is facing an extraordinary drought, causing water levels to fall to record lows throughout the area.
About the Amazon River
- Size and Ranking: The Amazon River is the largest river in the world by water volume and width, and it is the second-longest river after the Nile.
- Course: Its source is in the Andes Mountains, flowing into the Atlantic Ocean along Brazil’s northeastern coast.
River Basin:
- The Amazon has the largest drainage area of any river system.
- Its watershed includes Brazil, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, and Bolivia, with about two-thirds of the main river and most of its basin located in Brazil.
- The river’s width varies with the seasons, measuring 4 to 5 km during the dry season and expanding to 50 km in the wet season.
Tributaries
- Key tributaries include the Rio Negro, Madeira River, and Xingu River, among others.
Amazon Rainforest
- The river is surrounded by the Amazon Rainforest, which comprises about half of the Earth’s remaining rainforests and serves as the largest reserve of biological resources.
Environmental Importance
- Often called the “lungs of the Earth,” the Amazon plays a crucial role in regulating the planet’s oxygen and carbon cycles.



