Pharma sector in India
Why in News?
The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) in India has revoked the authority previously granted to State licensing authorities to issue no objection certificates (NOCs) for the manufacture of unapproved, banned, or new drugs for export purposes.
The Pharmaceutical Industry in India
Notable Achievements
- India, recognized as ‘the pharmacy of the world,’ plays a crucial role in global public health and universal healthcare access.
- Ranked 3rd worldwide in terms of pharmaceutical production by volume and 14th by value.
- Largest provider of generic medicines globally, supplying 20% of the global volume.
- Offers a wide range of generic brands across 60 therapeutic categories and is the leading vaccine manufacturer, producing 62% of the world’s vaccines.
- Majority of WHO’s vaccines are sourced from India, accounting for 70% of the essential immunization schedule.

Industry Scenario
- Allows 100% Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in the pharmaceutical sector.
- Industry valued at $50 billion in 2022-23, with exports constituting 50% of the production.
- Expected to reach $65 billion by 2024 and $130 billion by 2030.
- Major exporter, serving over 200 countries, including Africa, the US, and the UK.
- Drug and pharma product exports stood at $24.6 billion for 2021-22, witnessing a growth of 103% during 2014-22.
Centralization of the Licensing Authority
About
- CDSCO has withdrawn the authority from state licensing authorities to issue NOCs for exporting certain drugs.
- The head of CDSCO zonal offices will now grant NOCs, and manufacturers must obtain them through the Sugam Portal before receiving manufacturing licenses.
- Impact
- Significant for India’s readiness to benefit from an estimated $251 billion worth of off-patent drug sales in the upcoming decade.
- Centralization expected to formalize the industry, improve efficiency, and help achieve the target of $450 billion by 2047.
Challenges
- Addressing intellectual property rights and lack of research and development.
- Assessing various factors like political, economic, socio-cultural, technological, environmental, and legal aspects is crucial for understanding the opportunities and challenges in the Indian pharmaceutical market.
- Steps Taken to Ensure Quality Manufacturing
- Crackdown by Indian Govt.
- Government action against 18 drug companies for poor-quality manufacturing, including license cancellations and notices to non-compliant companies.
- Vision Pharma 2047: Aim to make India a global leader in affordable, innovative, and quality pharmaceuticals and medical devices.
- National Pharmaceutical Policy (2023): Draft policy focusing on fostering global pharmaceutical leadership, promoting self-reliance, advancing health equity and accessibility, enhancing regulatory efficiency, and attracting investments.
Cook Islands
The Cook Islands is leading efforts to explore the ocean depths for minerals essential in the production of batteries for electric vehicles.
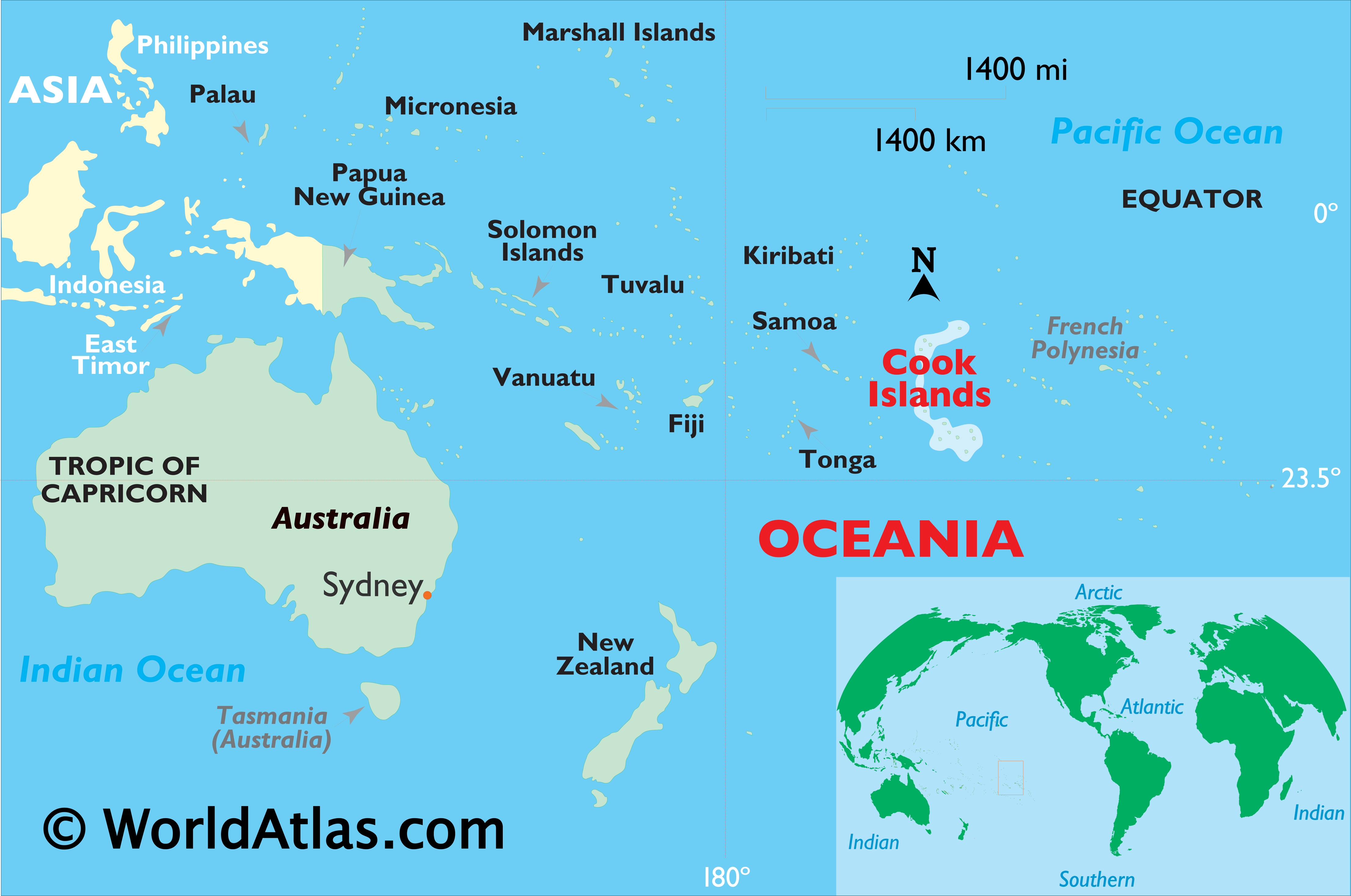
About Cook Islands:
- Political Status: It is a self-governing island state in free association with New Zealand.
- Location: Situated in the South Pacific Ocean, between Tonga to the west and French Polynesia to the east.
- Island Composition: Consists of 15 islands divided into a northern group of six islands and a southern group of nine islands.
- Northern Islands:
- Mostly low-lying coral atolls with sparse population.
- Includes Manihiki, Nassau, Penrhyn, Pukapuka, Rakahanga, and Suwarrow.
- Characterized by light vegetation and picturesque white sand beaches.
- Southern Islands:
- Comprised of larger, volcanic islands with higher elevation and higher population density.
- Includes Rarotonga, Aitutaki, Atiu, Mangaia, Manuae, Mauke, Mitiaro, Palmerston, and Takutea.
- Geographic Features: The highest point is Te Manga, reaching 652 meters on Rarotonga Island.
- Population Distribution: Majority of the population resides on the island of Rarotonga.
- Capital City: Avarua serves as the capital city and is located on Rarotonga Island.
Nerium oleander

Description:
- The Nerium oleander plant, commonly known as oleander or rosebay, is a rapidly growing evergreen, rounded shrub or small tree.
- In Kerala, it is referred to as arali and kanaveeram, and it is often grown along highways and beaches to serve as natural green fencing.
Origin
- Native to Europe and Asia, the Nerium oleander is cultivated worldwide in tropical, subtropical, and temperate regions.
Varieties and Features:
- Various varieties of Nerium oleander exist, each producing flowers of different colors.
- It is highly tolerant to deer and salt, making it suitable for coastal gardens.
- Additionally, it exhibits tolerance to heat, drought, wind, air pollution, and poor soil conditions.
Uses:
- Due to its drought tolerance, Nerium oleander is commonly used for ornamental and landscaping purposes.
- According to the Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India, oil extracted from the root bark can be utilized for treating skin diseases.
Toxicity:
- The plant contains toxic compounds such as oleandrin, neriin, and digitoxigenin, with oleandrin being the principal toxin.
- Ingestion or inhalation of smoke from burning oleander can be toxic due to the presence of cardiac glycosides, which exert pharmacological effects on cardiac muscle.
- Symptoms of oleander poisoning include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, rashes, confusion, dizziness, irregular heartbeat, slow heartbeat, and in severe cases, death.
- Contact with the plant’s sap, which is thick and gummy, can cause dermatitis upon skin contact.
DigiLocker
DigiLocker has emerged as a digital repository for official and governmental documents, and now students can access their scores and even acquire authenticated mark sheets through this platform.

About DigiLocker:
- Initiative and Establishment: DigiLocker was launched as a flagship initiative of the Ministry of Electronics & IT (MeitY) as part of the Digital India program in 2015.
- Government Approval and Security: It is an officially approved application by the government, maintained with stringent security protocols established by authorities.
- Operational Features: Functioning as a mobile application, DigiLocker serves as a digital repository for users’ records. It facilitates tasks such as passport applications, accessing academic marksheets, and providing identification during travel.
- Paper-Free Initiative: DigiLocker aligns with the Indian government’s endeavor towards a paperless administration. Its purpose is to enable users to access, verify, and store crucial documents digitally, ensuring easy retrieval and presentation when necessary.
- Legal Recognition: Documents issued through the DigiLocker system hold legal equivalence to their original physical counterparts, as per Rule 9A of the Information Technology (Preservation and Retention of Information by Intermediaries providing Digital Locker facilities) Rules, 2016.
- Security Measures: The platform employs robust security measures, including 2048 Bit RSA SSL encryption, multi-factor authentication (OTP verification), consent systems, timed logouts, and periodic security audits to safeguard users’ data.
FOOT ROT (BAKANE DISEASE)
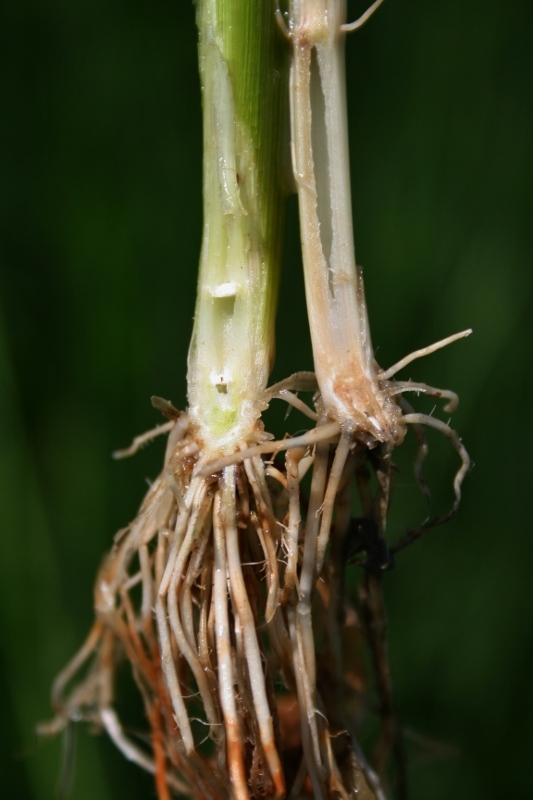

The Punjab Agricultural University (PAU) in Ludhiana has formulated a biocontrol agent called Trichoderma asperellum (2% WP) and successfully obtained registration for it from the Central Insecticides Board and Registration Committee (CIBRC).
About FOOT ROT (BAKANE DISEASE):
- Fungal Disease in Rice: Foot Rot, also referred to as Bakanae Disease, is a significant fungal infection that particularly affects rice, notably the Basmati variety.
- Causative Agent: The disease is caused by the fungus Gibberella fujikuroi, also known as Fusarium monoliforme.
- Affected Plant Parts: Primarily, Foot Rot targets the roots and basal stems of rice plants.
Characteristics of Foot Rot:
- Seedling Abnormalities: Affected seedlings exhibit abnormal elongation.
- Symptoms: Seedlings display a pale yellow coloration.
- Progression: Eventually, the seedlings desiccate and perish.
Impact of Foot Rot:
- Foot Rot not only diminishes crop yield but also poses health hazards due to mycotoxin contamination in the rice grains.
Management Strategies:
- Chemical Control: Historically, chemical fungicides were utilized to combat Foot Rot. However, due to environmental concerns and residue issues, alternative solutions are sought after.
- Biological Control: A recent development includes the registration of Trichoderma asperellum 2% WP by the Punjab Agricultural University (PAU) in Ludhiana. This eco-friendly approach involves applying Trichoderma to seeds or seedlings, which can suppress the growth of the Foot Rot pathogen.
- Cultural Practices: Implementing crop rotation, ensuring proper drainage, and avoiding waterlogged conditions can help mitigate the incidence of the disease.



