World Cybercrime Index
Why in News: After three years of thorough investigation, a global team of researchers has assembled the inaugural ‘World Cybercrime Index’, marking a significant milestone in the field of cybercrime analysis.
About World Cybercrime Index:
- Description: The index highlights the primary sources of cybercrime worldwide, ranking countries based on their contribution to cybercrime on a national scale.
- Partnership: Developed through collaboration between the University of Oxford and UNSW Canberra, this index marks a significant joint effort in cybercrime research.
- Data Collection: Information for the index was gathered from a survey involving 92 prominent cybercrime experts globally, specializing in intelligence gathering and investigations.
- Categorization: Approximately 100 countries are ranked based on various cybercrime categories such as ransomware, credit card theft, and scams.
Key Findings:
- Top Rankings: Russia leads the list of major cybercrime contributors, followed by Ukraine, China, the USA, Nigeria, and Romania.
- India’s Position: India holds the tenth position in the rankings, signifying its significance in the global cybercrime landscape.
- Association of Cybercrimes: Certain types of cybercrimes are linked with specific countries; for instance, the United States is associated with data and identity theft, while cybercrimes related to technical products or services often originate from China.
Source: TOI
Sungrazing Comets
Why in News: A minuscule “sungrazer” comet was spotted amidst the latest total solar eclipse.
About Sungrazing Comets:
- Definition: Sungrazing comets belong to a special category that ventures exceptionally close to the sun during their closest approach, known as perihelion.
- Proximity to Sun: To be classified as a sungrazer, a comet must approach within approximately 850,000 miles from the sun at perihelion, often coming even closer, sometimes within a few thousand miles.
- Challenges: The intense proximity to the sun poses significant challenges for these comets, including exposure to strong solar radiation, causing volatile substances like water to evaporate. Additionally, the radiation and solar wind contribute to the formation of their tails.
- Gravitational Stress: Sungrazing comets experience intense tidal forces and gravitational stress as they approach the sun, making survival difficult for many. Most sungrazers either evaporate in the hot solar atmosphere or disintegrate.
- Orbit: Majority of observed sungrazing comets follow a shared orbit known as the Kreutz Path, completing a single orbit every 800 years. These comets are part of the Kreutz Group, believed to be fragments of a larger comet shattered thousands of years ago. The farthest point of the Kreutz path is 160 times farther from the sun than Earth’s orbit.
Source: TH
Methanol
Why in News: Health authorities in the United States have recently issued recalls for multiple batches of hand sanitizers and aloe gels due to concerns regarding potential methanol exposure.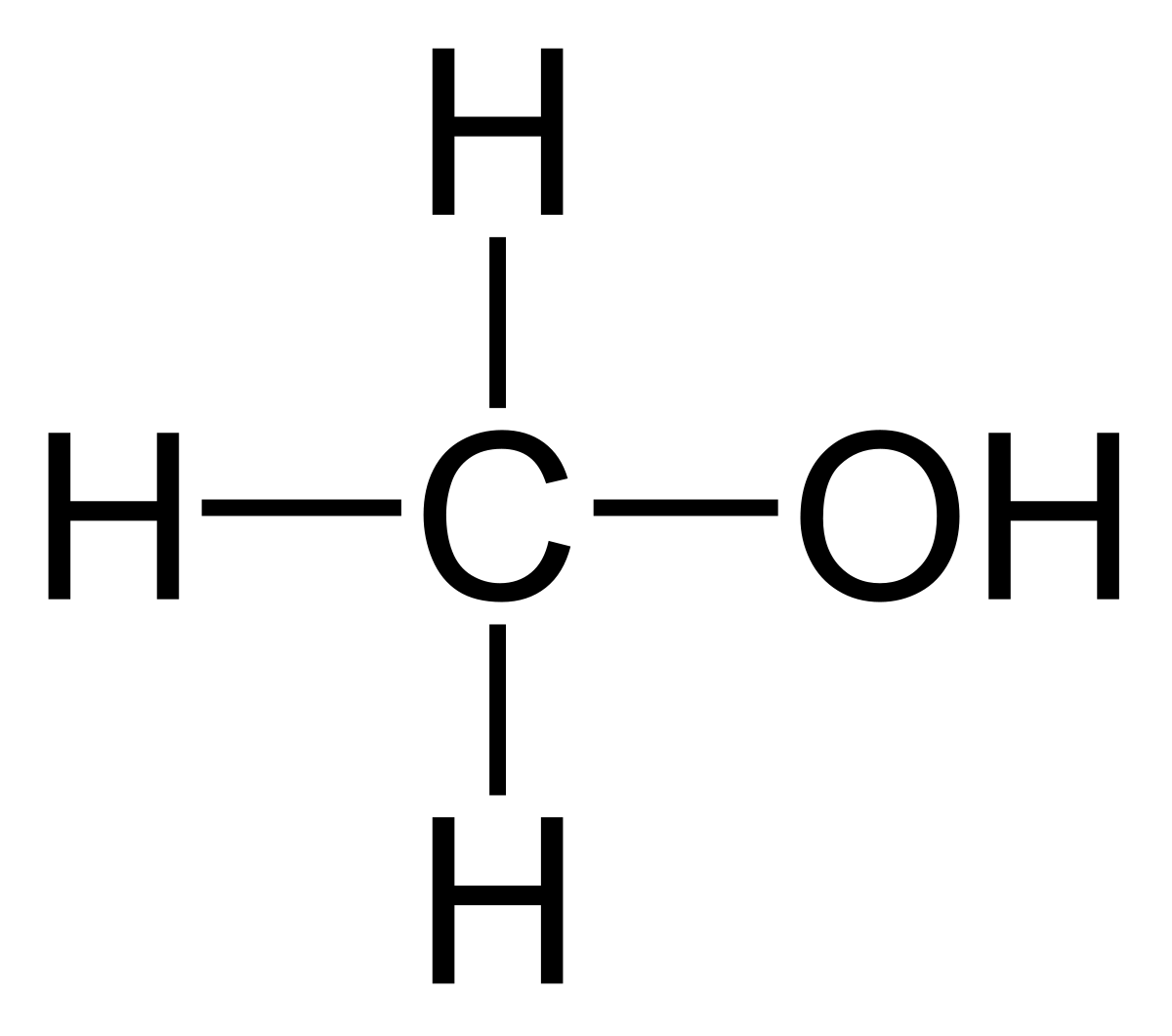
About Methanol:
- Physical Characteristics: Methanol presents as a colorless, moderately volatile liquid with a faintly sweet, sharp odor reminiscent of ethyl alcohol. Commonly referred to as wood alcohol, it readily mixes with water.
- Production: Methanol production typically involves the direct synthesis of carbon monoxide gas and hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst. Recently, there’s a trend towards using syngas, a blend of hydrogen and carbon monoxide derived from biomass, for methanol synthesis.
Benefits:
- Cost Efficiency: Methanol production is cost-effective compared to other alternative fuels.
- Safety: Methanol exhibits lower flammability risks in comparison to gasoline, enhancing safety.
- Energy Security: Methanol can be generated from various domestic carbon-based sources like biomass, natural gas, and coal, thus bolstering energy security.
- Applications: Methanol finds utility in various applications including chemical synthesis, fuel dehydration in automotive and aviation fuels, as a solvent in paint and plastic manufacturing, and as an ingredient in a diverse range of products.
Source: HT
Mange Disease
Why in News: The forest authorities are keeping a close watch on a spread of mange within a group of Asiatic wild dogs in the Mudumalai Tiger Reserve (MTR) located in the Nilgiris.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dog-patchy-mange-505072102-2000-7465de4bd8054207bdf7e6ee2f1d0155.jpg)
About Mange Disease:
- Definition: Mange is a skin condition affecting animals due to mite infestation, presenting symptoms like skin inflammation, itching, skin thickening, and hair loss.
- Severity: The most severe form of mange is caused by various types of the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, which also infects humans causing scabies.
- Variability: Mange occurs in all domestic animals, though certain types of mange mites affect only specific species.
- Transmission: Mange spreads among animals through direct contact or contact with objects previously in contact with infected animals. Most types of mange are treatable.
Key Facts about Asiatic Wild Dogs:
- Identification: Asiatic wild dogs, also known as Indian wild dogs, whistling dogs, red wolves, red dogs, and mountain wolves, are wild canids found in the forests of central, south, and southeast Asia.
Distribution:
- They inhabit Eastern and Southeastern Asia.
- Their range extends from Siberia to some Malaysian islands in the north and as far west as the Indian peninsula.
- In India, they form three clusters: the Western and Eastern Ghats, the central Indian landscape, and North East India.
![Dholes or Asiatic Wild Dog [UPSC Notes for Environment & Ecology]](https://cdn1.byjus.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/unnamed-11.jpg)
Conservation Status:
- Listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List.
- Protected under Schedule II of the Wildlife Protection Act 1972.
- Included in CITES Appendix II.



