Upper Karnali Hydro-electric Project
Why in News: The Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Ltd. (IREDA) has signed a Joint Venture Agreement with SJVN Ltd., GMR Energy Ltd., and Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA) to develop the 900 MW Upper Karnali Hydro-electric Project in Nepal.

About Upper Karnali Hydro-electric Project:
- Location and Capacity: A 900 MW run-of-the-river hydropower project on the Karnali River in Nepal.
- Power Supply and Duration: The project will provide power to Nepal, India, and Bangladesh for a contracted period of 25 years.
- Developing Entities: Developed by GMR Upper Karnali Hydro Power Limited (GUKHL), a subsidiary of GMR Group India, Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA), and SJVN Green Energy.
- Development Model: The project is being developed on a build-own-operate-transfer (BOOT) basis.
- Ownership Stakes: GUKHL owns 73% of the project, while NEA holds a 27% stake.
- Electricity Generation and Environmental Impact: The project is expected to generate 3,466 million units of electricity annually and reduce greenhouse gas emissions by approximately two million tons per year.
- Infrastructure Features: It will include a concrete gravity dam, headrace tunnels, fish pass, feeder tunnels, surge and pressure shafts, and silt flushing tunnels.
- Turbines and Capacity: The project will have 8 turbines, each with a 112.5 MW nameplate capacity.
- Development Timeline: Construction is expected to begin in 2027, with commercial operations starting by 2031.
SCOT Mission
Why in News: The Prime Minister recently praised the Indian space startup Digantara for the success of Mission SCOT.

About SCOT Mission:
- Mission Overview: SCOT (Space Camera for Object Tracking) is the inaugural mission of Digantara, an Indian space startup, focused on space surveillance.
- World’s First Commercial SSA Satellite: It is one of the world’s first commercial Space Situational Awareness (SSA) satellites.
- Launch Vehicle: The mission was launched aboard SpaceX’s Transporter-12 mission.
- Tracking Capabilities: SCOT is designed to track Resident Space Objects (RSOs).
- Orbit and Efficiency: It will be deployed in a sun-synchronous orbit, enhancing tracking efficiency in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) compared to existing sensors limited by fields of view (FoV), weather conditions, and geographical constraints.
- Surveillance Precision: SCOT will monitor objects as small as 5 cm in orbit, ensuring safer space operations.
- Support for National Security: The mission is backed by Aditya Birla Ventures and SIDBI and aims to support national security and space operations.
Points to Remember:
- Other Indian Startups in the Mission: Along with Digantara, two other Indian space startups have deployed their satellites aboard SpaceX’s Transporter-12 rocket launched from Vandenberg, California, US.
- Other Satellites Deployed: Bengaluru-based Pixxel launched the first three satellites of its Firefly constellation, while ELEVATION-1, a satellite for US-based Almagest Space Corporation, was developed by Hyderabad-based XDLINX Spacelabs.
Information Ratio
Why in News: The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) recently instructed mutual funds to include the information ratio (IR) of a scheme in their performance disclosures.

About Information Ratio (IR):
- Definition: The Information Ratio (IR) measures how a portfolio or financial asset performs relative to a benchmark, considering the volatility of its returns.
- Benchmark: The benchmark is typically a market index, such as Nifty 50, or an index representing a specific industry or market sector.
- Performance Comparison: The IR indicates how effectively a portfolio or asset is matching or exceeding the returns of its benchmark.
- Consistency in Performance: This ratio also reflects the consistency with which a portfolio can exceed the benchmark’s returns.
- Tracking Error: The ratio incorporates tracking error, or the standard deviation component, which shows how consistently a portfolio tracks and surpasses its benchmark.
- Tracking Error Significance: A low tracking error indicates consistency, while a high tracking error suggests greater volatility in performance.
- Formula for Calculation: IR = (Portfolio Rate of Returns – Benchmark Rate of Returns) / Tracking Error
Uses of Information Ratio:
- Performance Measure: The IR is primarily used by fund managers to evaluate portfolio performance.
- Comparison of Fund Managers: It is often used to compare the skills of fund managers with similar investment strategies.
- Investor Insights: The ratio helps investors understand a fund manager’s ability to generate consistent or abnormal returns over time.
- Fee Calculation: Some hedge funds and mutual funds use the IR to determine performance-related fees, such as performance fees.
Gulf of Aden
Why in News: The Defence Minister recently stated that threats in the Gulf of Aden, Red Sea, and waters near East African countries may rise, and the Indian Navy is working to enhance its presence to ensure the safety of sea routes.
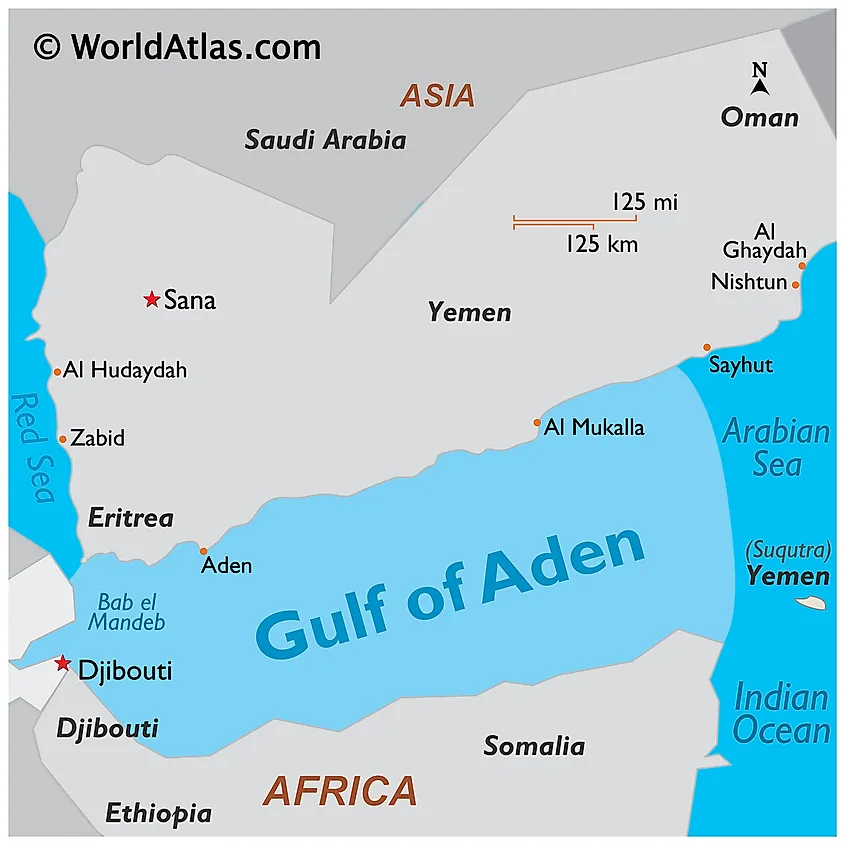
About Gulf of Aden:
- Location and Extent: The Gulf of Aden is an extension of the Indian Ocean, located between the Arabian Peninsula to the north and the Horn of Africa to the south. It connects the Red Sea to the Arabian Sea.
- Naming and Size: The gulf is named after the port city of Aden, located on Yemen’s coast. It is approximately 900 km long, 500 km wide, and covers about 410,000 sq.km.
- Geographical Boundaries:
South: Somalia and the Socotra Islands (Yemen)
North: Yemen
East: Arabian Sea
West: Djibouti
- Connections and Narrowing: The Gulf of Aden is connected to the Somali Sea to the south by the Guardafui Channel and to the Red Sea to the west by the Strait of Bab el Mandeb. It narrows into the Gulf of Tadjoura near Djibouti.
- Geological Features: The Sheba Ridge, an extension of the Indian Ocean ridge system, is a dominant terrain feature running through the middle of the gulf.
- Salinity: Compared to the neighboring Red Sea, the Gulf of Aden has lower salinity levels.
- Major Cities: Some key cities near the gulf include Aden, Mukalla, Ahnwar, Balhaf, Berbera, Bosaso, and Djibouti City.
- Strategic Importance: The gulf is a vital part of the Suez Canal shipping route, linking the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea.
- Global Shipping: Around 11% of seaborne petroleum passes through the Gulf of Aden, en route to the Mediterranean or Arabian Seas.



