Freshwater quest, the likely new gold hunt
Discoveries:
- In the 1960s, the U.S. Geological Survey drilled boreholes off the New Jersey coast and unexpectedly found freshwater.
- Scientists from Vietnam and other countries have also discovered underwater sources of freshwater.
- Example: A river was discovered under the sea at the bottom of the Black Sea, over 100 feet deep with a flow rate of about four miles per hour, making it one of the largest rivers in the world.

Statistics:
- The total volume of water on Earth is approximately 1.386 billion km³, with 97.5% being saltwater and 2.5% freshwater.
- Of this freshwater, only 0.3% is in liquid form on the surface, with the remainder underground, including beneath the ocean bed.
Future Exploration:
- Freshwater is a depleting resource, prompting countries to explore and exploit freshwater from their ocean beds.
- Countries are likely to extend exploration beyond their Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZ) into the “Area,” governed by Part XI of the United Nations Law of the Sea Convention, 1982 (UNCLOS).
- The “Area” under UNCLOS is defined as the seabed, ocean floor, and subsoil beyond national jurisdiction, considered the common heritage of mankind.
The Law of the Sea
UNCLOS:
- The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) is the comprehensive international law governing the oceans.
- Includes conventions on the Territorial Sea, Contiguous Zone, High Seas, Fishing and Conservation of Living Resources, and the Continental Shelf (Geneva Conventions on the Law of the Sea, 1958).

Provisions:
- Exploration and exploitation are limited to solid, liquid, or gaseous mineral resources in situ in the Area, including polymetallic nodules.
- The International Seabed Authority administers and controls activities in the Area.
- Exploration must comply with rules, regulations, and procedures established by the Authority.
Water Conflicts:
- Future conflicts are expected to be over water and territorial expansion.
- Freshwater wells, like oil wells, might be identified and capped for future use.
- India could lead efforts to find and preserve freshwater, benefiting humanity more than space colonization efforts on Mars and the moon.
Folds and faults
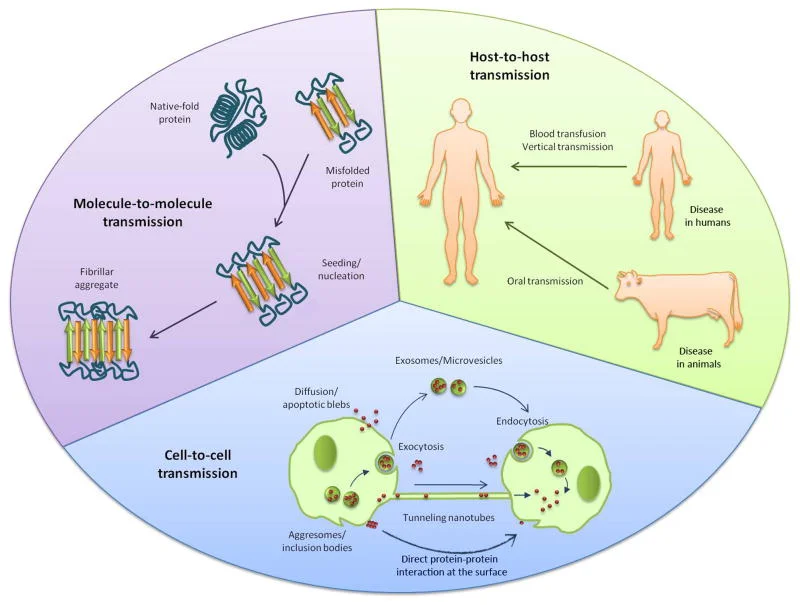
Protein Misfolding:
- Proteins are long chains of amino-acid residues that fold into specific shapes; misfolding can lead to severe diseases.
- Understanding how and why misfolding occurs is a key mystery in structural biology, known as the protein-folding problem.
AlphaFold Protein Model:
- In 2018, DeepMind, a Google subsidiary, developed AlphaFold, an AI tool to predict protein folding shapes.
- Recently, DeepMind released AlphaFold 3, which can predict shapes with nearly 80% accuracy and model DNA, RNA, ligands, and their modifications.
- While these machines predict protein structures, they do not explain why proteins fold in certain ways, a task that remains for human scientists.
Importance of AlphaFold:
- Many drugs fail because researchers cannot anticipate all interactions between the drug components and the body.
- Solving the protein-folding problem is crucial but won’t automatically improve drug success rates in clinical trials.
- The free use of AlphaFold 3 is currently limited, and its inner workings remain inaccessible for public examination or scrutiny.
India backs Palestine’s bid for full UN membership
News Context
- India voted in favor of a draft UN General Assembly resolution stating that Palestine is qualified and should be admitted as a full member of the United Nations.
General Assembly Session:
- The 193-member General Assembly held an emergency special session where the Arab Group resolution, titled ‘Admission of New Members to the United Nations,’ was presented by the UAE, as Chair of the Arab Group.
- The resolution supported the State of Palestine’s full membership in the UN.
- The resolution received 143 votes in favor, including from India, 9 against, and 25 abstentions, leading to applause in the UNGA hall.
- The resolution was in accordance with Article 4 of the UN Charter and recommended that the Security Council reconsider the matter favorably.
Historical Support:
- India was the first non-Arab state to recognize the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) as the sole legitimate representative of the Palestinian people in 1974.
- India was among the first countries to recognize the State of Palestine in 1996 and established its Representative Office to the Palestine Authority in Gaza, which was later moved to Ramallah in 2003.
Participation Rights:
- The additional rights and privileges of the State of Palestine will be effective from the 79th session of the General Assembly.
- These include the right to be seated among member states alphabetically, the right to make statements on behalf of a group, and the right to be present in meetings.
- As an observer state, Palestine does not have the right to vote in the General Assembly or to put forward its candidature to UN organs.