Preventive detention
Source: Economic Times
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy in News: The Supreme Court stressed the importance of curbing the arbitrary exercise of preventive detention authority, reversing a ruling made by the Telangana High Court.
Supreme Court’s Clarifications on Preventive Detention:
Purpose of Preventive Detention:
- Emphasized that preventive detention is intended to forestall future harm rather than serve as a punitive measure.
- Advocated for its application to be grounded in a meticulous examination of factual circumstances.
Severity of Preventive Detention:
- Highlighted that preventive detention constitutes a serious measure, cautioning against its routine or arbitrary invocation by authorities.
Clarity and Justification:
- Stressed the necessity for transparently stated grounds for detention and emphasized the importance of a comprehensive evaluation of pertinent facts in making detention decisions.

About Preventive Detention:
Definition and Purpose:
- Involves detaining individuals without trial or conviction, aiming to prevent future offenses rather than punish past ones.
- Governments enact such laws to ensure public safety and uphold social order.
Constitutional Safeguards in India:
- Article 22 of the Constitution safeguards individuals detained under preventive detention laws.
- Limits detention duration to three months unless extended by an Advisory Board.
Rights of Detainees:
- Entitled to be informed of the grounds of detention and provided with the opportunity to contest it.
Legislative Authority:
- Parliament holds exclusive authority to enact preventive detention laws for defense, foreign affairs, or national security reasons.
- Both Parliament and State Legislatures can enact laws for maintaining public order or essential services.
Relevant Laws in India:
- Laws such as the National Security Act (NSA) and the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA) allow for preventive detention for up to 12 months without formal charges, with periodic review by an advisory board.
Vietnam’s Mekong Delta
Source: TH
Why in News: Rising saltwater levels imperil Vietnam’s Mekong Delta, causing nearly $3 billion in annual crop losses. This threatens the region’s status as “Vietnam’s rice bowl,” particularly impacting agriculture in Ca Mau province.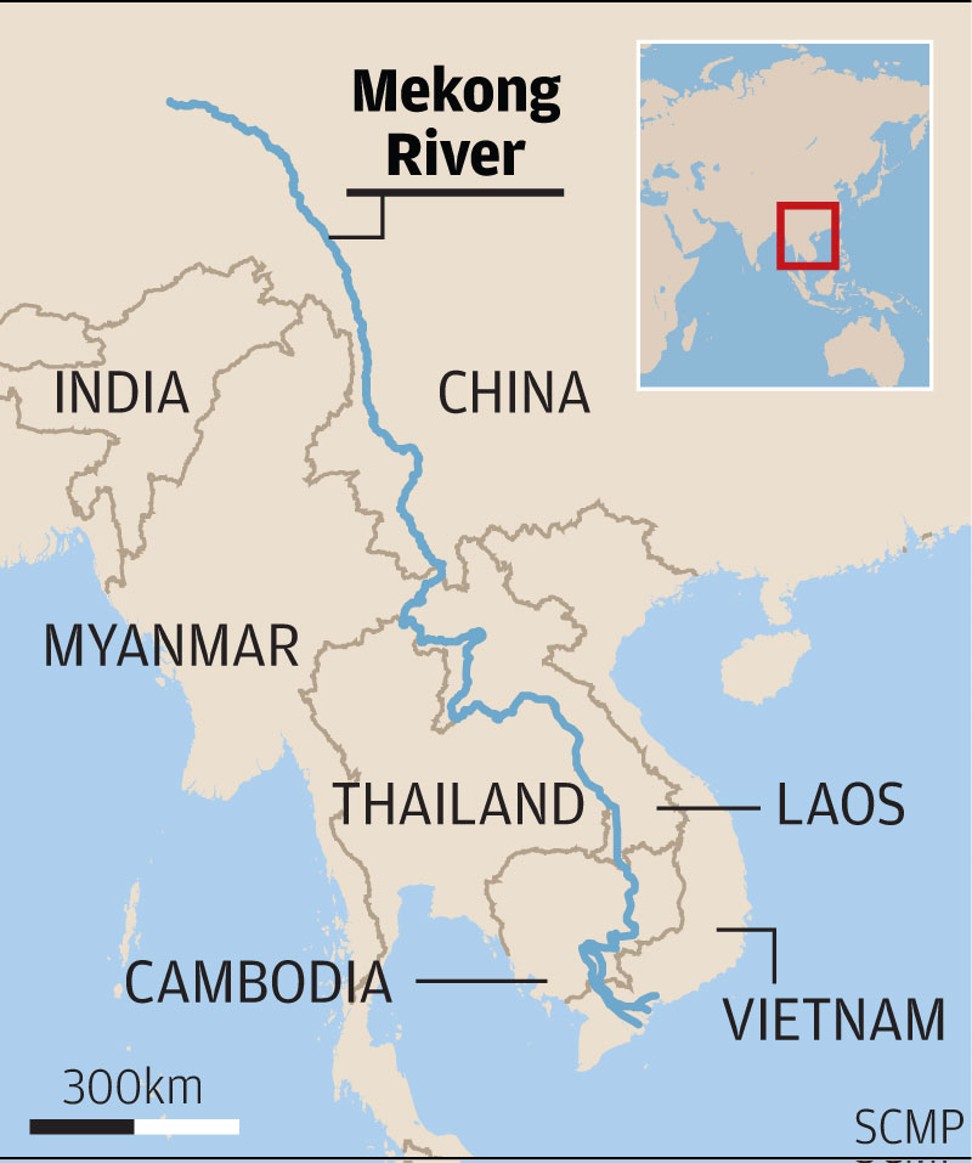
About the Mekong Delta in Vietnam:
Geographical Overview:
- Spans over 40,500 km2 as a wet coastal region where the Mekong River converges with the sea.
- Historically significant, dating back to the 4th century BC, it serves as a crucial agricultural and aquacultural hub.
Ecological Importance:
- Recognized for its rich biodiversity, the area faces vulnerabilities to climate change, including sea level rise and saltwater intrusion.
About the Mekong River:
- Geographical Extent: Stretches over 4,909 km, ranking among the world’s longest rivers, coursing through East and Southeast Asia.
- Origin and Course: Emerges from the Tibetan Plateau and traverses six countries before reaching southern Vietnam, where it nourishes the Mekong Delta.
- Navigational Challenges: Seasonal fluctuations and natural barriers impede navigation along its course, despite serving as a crucial trade route.
Lalita Kala Academy
Source: IE
Why in News: The Ministry of Culture has taken an unprecedented step by limiting the authority of Lalit Kala Akademi (LKA) Chairman, V Nagdas, preventing him from independently making administrative decisions. This includes matters such as appointments, recruitment, transfers, disciplinary actions, and financial decisions, requiring consultation with the ministry beforehand.
About Lalit Kala Akademi
Inauguration and Establishment:
- Founded on August 5, 1954, in New Delhi by Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, the then Minister for Education.
- Registered under the Societies Registration Act 1860 on March 11, 1957.
Focus and Mission:
- Established as the youngest of the three Akademies initiated by the Government of India, with a primary emphasis on activities within the Visual Arts realm.
Powers and Functions of LKA:
Promotion of Creative Arts:
- Encourages and promotes study and research in creative arts such as painting, sculpture, and graphics.
Coordination and Cooperation:
- Coordinates activities of regional art organizations and State Lalit Kala Akademis.
- Promotes cooperation among artists and art associations, fostering their development.
Establishment of Art Centers:
- Facilitates, where necessary, the establishment of Regional Art Centres.
Exchange of Ideas and Cultural Contacts
- Facilitates the exchange of ideas between various schools of art through conferences, seminars, exhibitions, etc., involving scholars, educationists, and art organizations nationally.
- Fosters cultural contacts within the country and internationally through art exhibitions, personnel exchange, etc.
Recognition and Support:
- Awards scholarships and prizes to deserving artists.
- Recognizes artists for outstanding achievements.
Preservation and Promotion of Traditional Arts:
- Promotes the study, research, and survey of folk, tribal, and traditional arts and crafts techniques.
- Preserves and promotes their art forms, organizing regional surveys and encouraging indigenous craftsmen, painters, and sculptors.
WHO launches ‘CoViNet’
Source: DTE
Why in News: The World Health Organization (WHO) has recently introduced a new network dedicated to coronaviruses, known as CoViNet.
About CoViNet:
- Global Surveillance Network: Comprises global laboratories specializing in human, animal, and environmental coronavirus surveillance.
- Identification and Monitoring: Tasked with identifying and monitoring potentially emerging novel coronaviruses.
- Expanded Surveillance Scope: Incorporates animal health and environmental surveillance, facilitating timely risk assessment to inform WHO policies and protective measures.
- Support in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Aims to bolster laboratory infrastructure in low- and middle-income countries to monitor MERS-CoV and other emerging coronaviruses of public health significance.
- Data Utilization: Data generated by CoViNet guides the work of WHO’s Technical Advisory Groups on Viral Evolution and Vaccine Composition, ensuring global health policies and tools are grounded in the latest scientific insights.
Membership and Composition:
- Currently consists of 36 laboratories spanning 21 countries across all six WHO regions.
- Includes notable Indian laboratories such as the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, the Indian Council of Medical Research-National Institute of Virology in Pune, and the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute.
Key Facts about the World Health Organization:
Establishment and Mission: Founded in 1948 as a specialized agency of the United Nations, dedicated to promoting health, ensuring global safety, and serving vulnerable populations.
Governance Structure:
- Membership comprises 194 member states.
- World Health Assembly (WHA) serves as the highest decision-making body, representing all member states.
- Secretariat implements WHA-approved policies and programs.
- Director-General oversees the WHA and is supported by a senior management team.
Regional Presence: Operates through six regional offices: Africa, the Americas, Southeast Asia, Europe, Eastern Mediterranean, and Western Pacific.






