Mumps
Source: TH
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy in News: Mumps, a sudden viral illness traditionally impacting children, has been rapidly spreading throughout Kerala over the last several months.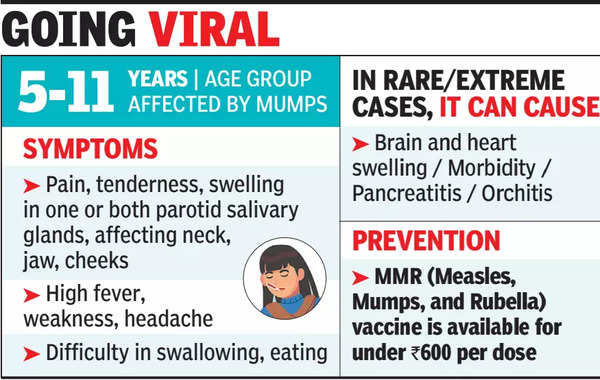
About Mumps
- Nature of the Disease: Mumps is a viral illness primarily affecting children and adolescents, characterized by fever, headache, and swollen salivary glands on both sides of the face.
- Treatment and Recovery: There is no specific treatment for mumps, and patients typically recover within two weeks through rest and managing symptoms.
- Underreporting of Cases: Due to about half of infected children showing classical symptoms and nearly 30% remaining asymptomatic, many cases of mumps go unreported, suggesting a significant underestimation of actual cases in the community.
- Public Health Perspective: Measles, with its potential for severe complications, has historically garnered more attention in public health efforts compared to mumps.
- Vaccination Status: Despite being preventable through vaccination, mumps hasn’t been included in the Universal Immunisation Programme (UIP) due to its low mortality rate and perceived lower public health impact.
- Importance of Public Awareness: Health officials emphasize the importance of raising public awareness about mumps and the necessity of isolating infected individuals to reduce disease transmission.
- Transmission Dynamics: Mumps can be transmitted before symptoms appear, necessitating a three-week isolation period for infected individuals to mitigate disease spread.
EU’s first Digital Markets Act
Source: IE
Why in News: European antitrust regulators recently announced an investigation into Apple, Alphabet’s Google, and Meta Platforms for possible violations of the EU’s newly enacted Digital Markets Act.
About Digital Markets Act (DMA)
- Objective of DMA: The DMA is an EU law designed to promote fairness and competition in the digital sector, with the goal of creating a safer internet, empowering citizens, enhancing consumer protections, and improving the quality of digital services.
- Identification of Gatekeepers: It establishes specific criteria to identify “gatekeepers,” which are large digital platforms offering core services like online search engines, app stores, and messenger services.
- Obligations and Prohibitions: Gatekeepers are required to comply with a set of obligations (do’s) and prohibitions (don’ts) outlined in the DMA.
- Regulation of Gatekeeper Power: The DMA is among the first regulatory measures aimed at comprehensively regulating the dominant power of major digital companies.
Key Measures
- Tighter restrictions on the use of personal data by digital gatekeepers, requiring explicit user consent for tracking activities for advertising purposes.
- Collaboration between messaging services and social media platforms, potentially allowing users of one platform to communicate directly with users of another (e.g., Meta-owned WhatsApp messaging users communicating with users of Telegram).
- Providing users with the option to uninstall preloaded applications on devices.
- Prohibition on gatekeepers favoring their own products or services over others in online search rankings.
INTERNATIONAL ASTRONOMICAL UNION (IAU)
Source: BS
Why in News: The International Astronomical Union (IAU) has given approval for the name ‘Shiva Shakti’ to be used as the landing site designation for Chandrayaan-3.
About International Astronomical Union (IAU)
- Governing Body: The International Astronomical Union (IAU) is a significant organization overseeing global professional astronomical endeavors.
- Establishment and History: Founded in 1919, the IAU was the first among several international unions dedicated to advancing specific branches of science.
- Headquarters: The IAU is headquartered in Paris, France.
- Mission: Its mission is to advance and protect the field of astronomy comprehensively, including research, communication, education, and development, through international collaboration.
- Structure: The IAU comprises divisions, commissions, and working groups, each representing distinct areas of astronomical research, teaching, and related activities.
- Naming Authority: It is the sole professionally recognized organization responsible for naming celestial bodies, based on factors such as merit, historical significance, or the privilege of discovery.
- General Assembly: The IAU convenes a general assembly every three years at various global locations, where professional astronomers gather to discuss research, foster collaborations, and address matters of professional importance.
- Promotion of Astronomy: Additionally, the IAU promotes astronomy through research, education, and public outreach efforts aimed at engaging and informing the general public about the field.
Kalyana Chalukya dynasty
Source: TH
Why in News: A Kannada inscription dating back 900 years, originating from the Kalyana Chalukya dynasty, has been discovered in Gangapuram, a temple town located in Telangana.
About Chalukya Dynasty:
- Historical Background: The Chalukyas governed the central Indian plateau of the Deccan from the 6th to the 12th centuries, existing as three closely related yet distinct dynasties.
- Dynastic Divisions: The Chalukyas consisted of the Chalukyas of Badami (6th-8th centuries), the Western Chalukyas or Chalukyas of Kalyani, and the Eastern Chalukyas or Chalukyas of Vengi.
Key Facts about Chalukyas of Kalyani:
- They were predominantly a Kannadiga dynasty, named after their capital city, Kalyani, located in modern-day Bidar district, Karnataka.
- Tailapa II founded the empire, initially serving as a feudatory under the Rashtrakuta Empire, governing Tardavadi in Bijapur district, Karnataka.
- Under Vikramaditya VI (1076-1126 CE), the dynasty reached its zenith, referred to as the ‘Chalukya Vikrama era’.
Military Exploits:
- Vikramaditya VI expanded his influence by subduing northern feudatories and defeating the Chola dynasty in battles, notably at Vengi in 1093 and 1118.
Decline:
- After Vikramaditya VI’s death, consistent conflicts with the Cholas weakened both empires, leading to internal rebellions.
- The decline accelerated after 1126, culminating in disintegration during Jagadhekamalla II’s reign.
Administration, Art, and Architecture:
- Administration involved passing power to male heirs or brothers, with the kingdom managed by feudatories in their absence.
- The dynasty was tolerant of Buddhism and Jainism, contributing significantly to Kannada and Telugu literature.
- They minted pagoda coins with Kannada inscriptions and developed a unique architectural style known as the ‘Gadag style’, seen in temples like Mallikarjuna temple in Bellary and Siddeshvara temple in Haveri.






